ADENOMYOSIS OF THE GALLBLADDER
Transcription
ADENOMYOSIS OF THE GALLBLADDER
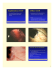
ADENOMYOSIS OF THE GALLBLADDER Abbas Al-Kurd, MD Department of Surgery, Hadassah-Hebrew University Medical Center, Mount Scopus, Jerusalem, Israel Case 1 – 9/2008 • 54 yr old female • PMHx: Hyperlipidemia • Postprandial RUQ pain, radiating to back + nausea • Several months • U/S – GB 2x7 cm. Wall severely thickened, irregular, several echogenic foci. No stones. Two LN’s at porta hepatis 0.7x1.5 cm. • CT – Contracted GB, severe mural thickening, irregular, several intramural cystic areas. No invasion to liver. Two LN’s inferior to PV – 1.5 cm. No biliary dilation. • CEA 3.28 • CA 19-9 8.35 • LFT’s nL 2/10/2008 – Laparotomy • Hard GB mass, peritoneal aspect of GB • Enlarged regional LN’s • Liver normal • Radical Cholecystectomy Case 2 – 9/2012 • 56 yr old female • PMHx – Hyperlipidemia, smoking • RUQ pain + nausea, 3 months. • U/S – SOL in GB, 1.3X2.4 cm, cystic areas • DDx: GB Carcinoma vs Adenomyosis • Markers nL 4/9/2012 – Laparotomy • 2 cm solid mass at hepatic aspect of the fundus of GB • Not clear if it invades liver • Enlarged retroduodenal LN 2.5 cm • Radical cholecystectomy Case 3 – 7/7/2015 • 49 yr old female • PMHx: Smoker • RUQ pain, recurrent attacks since 3 months • U/S: • CEA 7.26 • CA 19-9 11.9 • LFT’s nL 9/7/2015 – Laparotomy • 3 cm soft mass at peritoneal aspect of fundus/body • No enlarged LN’s • Radical Cholecystectomy Gallbladder Adenomyomatosis • Benign • Relatively common • Incidence: 2–8% (cholecystectomy specimens) • More in females, 50’s – 60’s • Rarely symptomatic • 75 – 90% cholelithiasis • Adenomyomatosis • Adenomyosis • Adenomyoma • Hyperplastic cholecystosis • Diverticular disease of GB • Intramural diverticulosis of GB • Cholecystitis cystica • Cholecystitis glandularis proliferans “Adenomyomatosis” • Benign hyperplastic lesion characterized by: – excessive proliferation of surface epithelium – invagination into the thickened muscular layer or deeper – wall thickening – intramural diverticulosis – Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses Types Annular Fundal Segmental Diffuse Diagnosis • U/S – Mural thickening – Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses – Comet-tail artifacts – Twinkling artifacts (doppler) • CT – Mural thickening and enhancement – Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses • MRI/MRCP – Mural thickening, sinuses – Pearl necklace sign – Diamond ring sign • N = 20 • Surgically proven adenomyomatosis • Accuracy: – U/S 66% – CT 75% – MRI 93% • Addition of high mgHz imaging to conventional low mgHz imaging • Harmonics, compounding techniques, and speckle reduction imaging • 45-Adenomyomatosis • 28-Carcinoma Sensitivity – 80.0% Specificity – 85.7% Accuracy – 82.2% • Adenomyomatosis 13 • Carcinoma 27 • Sensitivity: – HRUS 73.1% – MDCT 50.0% – MRI 80.8% Carcinoma Risk? • Historically: benign condition • Potential role in carcinogenesis? Katoh T, Nakai T, Hayashi S, Satake T. Noninvasive carcinoma of the gallbladder arising in localized type adenomyomatosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jun;83(6):670-4. Kurihara K, Mizuseki K, Ninomiya T, Shoji I, Kajiwara S. Carcinoma of the gall-bladder arising in adenomyomatosis. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1993 Jan-Feb;43(1-2):82-5. Sakurai T, Saji Y, Kazui K, Yamaga S, Hirose K, Shinohara T, Uchino J. A case of early carcinoma of the gall-bladder arising in adenomyomatosis detected by endoscopic ultrasonography. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1995 Sep;92(9):1304-8. Relationship between gallbladder carcinoma and the segmental type of adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder. Ootani T, Shirai Y, Tsukada K, Muto T. Cancer. 1992 Jun 1;69(11):2647-52. • 3197 consecutive cholecystectomies • Adenomyomatosis 279 (8.7%) – Segmental – 188 • 6.4% malignancy • 3.1% malignancy in others • P < 0.025 High risk of gallbladder carcinoma in elderly patients with segmental adenomyomatosis of the gallbladder. Nabatame N, Shirai Y, Nishimura A, Yokoyama N, Wakai T, Hatakeyama K. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Dec;23(4):593-8. • 4,560 consecutive cholecystectomies • Segmental adenomyomatosis – 334 (7.3%) • Carcinoma 6.6% • Others Carcinoma 4.3% • More in age >60 Management • No clear guidelines • Symptomatic Surgery • Unclear diagnosis/possible malignancy Surgery • Approach? Conclusion • Benign • Malignant potential? • Radiologic diagnosis • Differentiation from carcinoma • Management controversial