Hand-in-Hand 2006
Transcription
Hand-in-Hand 2006
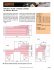
2006 Foreword Automakers Seek Closer ASEAN-Japan Cooperation for the Years Ahead New vehicle sales in the ASEAN market (Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand) in 2005 totalled 2 million units, a 14 percent increase over the previous year, further demonstrating that ASEAN is one of the world’s fastest growing automobile markets. Considering also the rapid motorization in China and India, there is no doubt that Asia, including the ASEAN region, is the growth center of the worldwide automobile market and in the global spotlight. This booklet describes the activities of Japanese automakers in the ASEAN region in recent years. The latest available data indicates that in 2005, member companies of the Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA) and their local partners produced 2,027,123 motor vehicles in and exported 405,511 units from ASEAN countries. The direct employment generated by these activities created jobs for over 86,000 people within ASEAN. The partnership between the ASEAN and 2 Japanese motor industries dates back more than forty years. That long period saw times of economic difficulty, including the Asian currency crisis, but over those many years the Japanese automobile industry steadily invested in the ASEAN region, expanding vehicle production, sales and employment there. For ASEAN auto industry players, the speed of economic development in ASEAN’s competitor countries and the speed of response to changes taking place within the industry are crucial factors to take into account. The pace of such development and change underscores the fact that timely action is critical for the ASEAN auto industry, particularly in view of ASEAN integration through AFTA and the trend to establish economic partnership agreements (EPAs). The Japanese automobile industry would like to strengthen its ties with the industry in ASEAN so that this partnership can take a leading global role in automotive production in the years ahead. Contents Foreword 2 Contents 3 2005 Production Facilities in ASEAN 4 Steady Growth in Production in ASEAN Export Expansion in ASEAN 9 JAMA's Activities in ASEAN 10 The History of Japanese Automakers in ASEAN 14 3 2005 Production Facilities in ASEAN Indonesia . Celebes Sea Kuantan Medan 1 4 5 6 7 akarta 8 9 10 11 15 16 13 Johor Bahru Bukit Indah Sulawesi Banjarmasin Jawa Sea Jakarta INDONESIA wa or Lesser Sunda Is. Su m ba Denpasar Fl . ba Is Surabaya Yogyakarta k a Semarang m Bandung Su nd B bo Jawa m Su Lo er Ujung Pandang (Makassar) li at sar Bangka Belitung re Str Balikpapan Sumatera G Samarinda es 2 12 Borneo (Kalimantan) kas Padang Manado . SINGAPORE 3 14 Karawang Ma Bekasi Ba J Kuala Lumpur ■AUTOMOBILE PRODUCTION COMPANIES ●COMPONENTS MANUFACTURING COMPANIES Automaker Company Products Established Production s Employees Capital Investment Headquarter’ Stake 4,862 RP 338.85 billion 68.13% 1 Daihatsu P. T. Astra Daihatsu Motor Taruna, Zebra, F, Ceria, Xenia, Toyota Avanza, engines 1992 104,418 units 2 Hino P. T. Hino Motors Manufacturing Indonesia medium & heavy-duty trucks and buses 2003 5,092 units 3 Honda P. T. Honda Prospect Motor Civic, CR-V, Stream, Jazz 1977 40,380 units 2,810 US$ 70 million 51% 4 Isuzu P. T. Pantja Motor Panther, Elf, F-series 1974 24,178 units 428 RP 92 billion 12.5% 5 Mitsubishi P. T. Krama Yudha Kesuma Motors (KKM) Galant, Kuda 1972 2,160 units(*1) 330 RP 1,500 million 0%(*2) 6 Mitsubishi 7 Mitsubishi Fuso P. T. Krama Yudha Ratu Motor (KRM) Colt T-120SS, Colt L300 Canter, Fuso 1973 44,064 units 1,176 39,079 units 280 280 Terrano, X-trail, Serena 2001 11,247 units 9 Nissan Diesel P. T. Astra Nissan Diesel Indonesia trucks and buses 1996 1,926 units 10 Suzuki Baleno, Carry, Futura, Jimny, Escudo, Karimun, Aerio, APV 1990 104,133 units 8 Nissan P. T. Nissan Motor Indonesia P. T. Indomobil Suzuki International 11 Toyota P. T. Toyota Motor Manufacturing Indonesia Kijang Innova, Kijang P/U, engines 1971 12 Honda P. T. Honda Precision Parts Manufacturing automatic transmissions, engine valves 2002 13 Isuzu P. T. Mesin Isuzu Indonesia engines 1983 14 Isuzu P. T. Asian Isuzu Casting Center casting parts 1997 15 Mitsubishi P. T. Mitsubishi Krama Yudha Motors & engines, body parts 1973 16 Mitsubishi Fuso Manufacturing (MKM) 315 US$ 47.8 million (*4) 98,257 units 232,831 units(*5) 172,169 units(*6) 7,533,174 units(*7) 27,078 units 119,033 units(*8) 22,225 units(*9) 47,232 units 39,633 units 90% RP 12,000 million 0%(*3) US$ 56 million 83.3% 103 RP 62.84 billion 12.5% 3,756 US$ 45 million 90% 3,895 RP 19.5 billion 95% 869 US$ 64 million 100% 175 RP 13 billion 38.2% 362 RP 107 billion 77.5% 893 RP 11,451 million (*1) KKM ended its production in September 2005. (*2) Technology Tie-up (*3) Assembly Consignment (*4) CBU (*5) engines (*6) automatic transmissions (*7) engine valves (*8) cylinder blocks (*9) cylinder heads 4 32.3% 0% Malaysia Malaysia Phnom Penh Nha Trang 5 Pekan Rawang 3 Petaling Jaya 7 8 9 Kuala Lumpur Palawan 6 10 Shah Alam 2 11 Ho Chi Minh (Saigon) Sihanoukville Indonesia Rach Gia Can Tho 1 Gulf of Thailand 4 Phuket Songkhla Melaka M 12 Johor Bahru al ay Kota Bharu Sandakan Pe of Ipoh ca ac al M n. r. St George Town (Penang) Bandar Seri Begawan MALAYSIA BRUNEI Kuantan Medan Kuala Lumpur Borneo (Kalimantan) ar Sumatera ■AUTOMOBILE PRODUCTION COMPANIES ●COMPONENTS MANUFACTURING COMPANIES Automaker Company Products Established Production s Employees Capital Investment Headquarter’ Stake 1 Daihatsu Daihatsu Malaysia Sdn. Bhd. Delta, Hijet maxx 1980 5,587 units 597 2 Daihatsu Perodua Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. Kancil, Kelisa, Kenari, Rusa, Kembara, Myvi 1993 180,578 units 7,066 3 Hino Hino Motors (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd. Dutro, Validus, buses 1989 2,141 units 80 4 Honda Honda Malaysia Sdn. Bhd. Accord, Civic, City, CR-V 2000 22,740 units 5 Isuzu Malaysian Truck and Bus Sdn. Bhd. TF, UBS, N*R, F*R, CXZ 1997 3,192 units 6 Mitsubishi Perusahaan Otomobile Nasional Sdn. Saga, Wira, Satria, Putra, Perdana, Arena Berhad (Proton) 1983 7 Mitsubishi Fuso DaimlerChrysler Malaysia Sdn. Bhd. Canter, Fuso 2005 RM 20 million 28.5% RM 140 million 26% (*1) RM 15 million 58% 1,423 RM 98 million 51% 940 RM 100 million 20% 187,512 units 11,000 RM 549.2 million 0% (*2) RM 134.7 million 0% 1,140 RM 1 million 0% RM 7.5 million 0% (*4) 988 units 1,300 Sentra, Cefiro, Vanette, Serena, X-trail, Tan Chong Motor Assemblies Sdn. Bhd. Frontier 9 Nissan Diesel trucks and buses 1974 Camry, Corolla, Hiace, Hilux, Vios, Innova, Fortuner, engines 1968 54,684 units 10,483 units(*3) 3,236 870 28,437 units 8 Nissan 2,418 units 10 Toyota Assembly Services Sdn. Bhd. 11 Daihatsu Perodua Engine Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. engines 1996 --- 12 Honda Honda Autoparts Manufacturing (M) bumpers, instrument panels, others Sdn. Bhd. 1992 236,200 units(*6) 190,800 units(*7) RM 40 million 26% (*5) 134 RM 25.8 million 51% (*1)(*5) Perodua Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. and Perodua Engine Manufacturing Sdn. Bhd. are 51% owned by PCSB (Perodua Auto Corporation Sdn. Bhd.), a holding company in which Daihatsu acquired a 51% equity stake. (*2) Number of employees represents figures for Malaysian Truck & Bus (MTB), which consigns for production in Malaysia (including passenger cars, other company’s products). (*3) engines (*4) Assembly Services Sdn. Bhd. is 100% owned by UMWT (United Motor Works Toyota), an affiliate company in which Toyota acquired a 50% equity stake. (*6) bumpers (*7) instrument panels and others 5 2005 Production Facilities in ASEAN The Philippines Babuyan Is. 8 Metro Manila 6 Canlubang 1 Makti 4 5 Rizal 10 Binan 2 Santa Rosa 3 7 9 11 12 13 Baguio Luzon Laguna Philippine Sea Manila PHILIPPINES Mindoro Samar Panay Iloilo South C hina Sea Bacolod Leyte Cebu Negros Palawan Sulu Sea Mindanao Davao Zamboanga P Sandakan BRUNEI ■AUTOMOBILE PRODUCTION COMPANIES ●COMPONENTS MANUFACTURING COMPANIES Automaker Company Products Established Production s Employees Capital Investment Headquarter’ Stake 1 Hino Pilipinas Hino Inc. trucks and buses for Category IV-V 1975 258 units 158 P 187.5 million 14.9% 2 7,440 units 676 P 770 million 54% 9,170 units 661 P 1,000 million 35% 704 P 1,640 million Honda Honda Cars Philippines Inc. Civic, City, CR-V 1990 3 Isuzu Isuzu Philippines Corporation Alterra, Crosswind, D-max, N-series, F-series, buses 1995 4 Mitsubishi Mitsubishi Motors Philippines 5 Mitsubishi Fuso Corporation (MMPC) 6 Nissan 7 Pajero, L300, Adventure 10,306 units 1963 Canter, Fuso 51% 0% 411 units Universal Motors Corporation Datsun, Safari, Terrano, Caravan 1954 2,771 units 309 P 154 million 0% (*1) Nissan Motor Philippines Inc. Sunny, Cefiro, X-trail 1982 5,103 units 363 P 1,845 million 5.36% 1981 250 units 80 P 1,570 million 1.6% 1989 17,826 units 1,287 P 2,423 million 34% 8 Nissan Diesel Columbian Motors Corporation trucks and buses 9 Toyota Toyota Motor Philippines Corp. Camry, Corolla, Innova 10 Honda Honda Parts Manufacturing Corp. manual transmissions 1992 80,738 units 349 P 810.8 million 100% 11 Isuzu Isuzu Autoparts Manufacturing Corporation transmissions 1996 189,157 units 475 P 442 million 0% (*2) 12 Mitsubishi Asian Transmission Corporation (ATC) transmissions, engines, axles 1973 404,035 units 485 P 350 million 5% 1990 (*3) P 1,000 million 95% 13 Toyota Toyota Autoparts Philippines Inc. transmissions, constant velocity joints 220,731 units 580 (*1) Technology Tie-up (*2) Isuzu Autoparts Manufacturing Corporation is 100% owned by IMA (Isuzu Motors Asia) Ltd., an affiliate company in which Isuzu acquired a 100% equity stake. (*3) transmissions 6 The Philippines Thailand Thailand MYANMAR (BURMA) LAOS Haikou Luang Prabang Chiang Mai Gulf of TongkingHainan Vientiane Yangon (Rangoon) Tak Udon Thani s. man I Bangkok Ubon Ratchathani 1 Tonle Sap g on Nakhon Ratchasima Hue ek Gulf of Martaban THAILAND M Moulmein Da Nang Ayutthaya 5 6 Pathumthani 10 Bangkok 3 Samrong-Tai 9 Gateway 7 8 S amutprakarn 9 12 13 Chonburi 2 Qui Nhon CAMBODIA VIETNAM Anda Phnom Penh Andaman Sea Gulf of Thailand bar Nico Rayong Rach Gia Can Tho Sout h C hi na Sea Palawan Phuket M Songkhla al Is. Kota Bharu ay George Town (Penang) Pe Banda Aceh Ho Chi Minh (Saigon) Sihanoukville 4 11 Nha Trang Sandakan BRUNEI n Ipoh ■AUTOMOBILE PRODUCTION COMPANIES ●COMPONENTS MANUFACTURING COMPANIES Automaker Company 1 Hino Hino Motor Manufacturing (Thailand) Ltd. Honda Automobile (Thailand) Co., Ltd. 3 Isuzu Isuzu Motors Co., (Thailand) Ltd. 4 Mazda AutoAlliance (Thailand) Co., Ltd. Mitsubishi Motors (Thailand) Co.,Ltd. 5 Mitsubishi (MMTh) Mitsubishi Fuso Truck (Thailand) Co., Ltd. 6 Mitsubishi Fuso (MFTT) Siam Nissan Automobile Co., Ltd. 7 Nissan Siam Motors & Nissan Co., Ltd. 8 Nissan Diesel Nissan Diesel (Thailand) Co., Ltd. 9 Toyota Toyota Motor Thailand Co., Ltd. 10 Isuzu Isuzu Engine Manufacturing Co., (Thailand) Ltd. 2 Honda 11 Nissan Siam Metal Technology Co., Ltd. Nissan Powertrain (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (*1) 12 Nissan s Employees Capital Investment Headquarter’ Stake Established Production medium & heavy-duty trucks and buses Accord, Civic, City, CR-V, Jazz pick-ups, N-series, F-series Mazda B-Series, Ford Ranger, Everest 2003 1983 1966 1995 7,997 units 104,660 units 185,711 units 109,608 units 3,066 3,745 3,473 2,978 Lancer, Strada, Space Wagon, Triton 1987 159,214 units 4,074 Bht. 7,000 million 99.79% Canter, Fuso 2004 2,194 units Frontier, Wingroad Tiana, Sunny trucks and buses Camry, Corolla, Vios, Wish, Hilux Vigo, Fortuner, engines diesel engines knuckle spindles, knuckle arms, rear axle shafts, forging parts for automobile engine unit (assembly) 1973 1962 1987 1962 1987 engine parts machining (cylinder blocks, cylinder heads) Design/manufacturing of stamping die and body ass'y jig for autobody. Parts production of stamping and sub-ass'y using above-mentioned dies and jigs. Siam Toyota Manufacturing Co., Ltd. diesel/gasoline engines, propellar shifts, casting (blocks, heads) SNN Tools & Dies Co., Ltd. 13 Toyota Products Bht. 2,000 million Bht. 5,460 million Bht. 8,500 million Bht. 5,000 million 80% 91.5% 6.7% 45% 205 Bht. 500 million 100% 1,374 units 366,935 units 216,198 units Bht. 1,930.91 million Bht. 13.33 million 184 Bht. 1,896 million 5,909 Bht. 7,520 million 1,019 Bht. 1,025 million 75% 75% 0% 86.4% 1.4% 1996 5,510,284 units 250 Bht. 617 million 25% 1987 45,021 units 21,163 units (*2) 26,404 units (*3) 241 Bht. 1,400 million 35% 1989 --- 328 Bht. 135 million 27.8% 1987 403,873 units (*4) 2,256 Bht. 850 million 96% 44,022 units 1,515 (*1)Thai Automotive Industry Co., Ltd. became Nissan Powertrain (Thailand) Co., Ltd. in December 2004. (*2) cylinder blocks (*3) cylinder heads (*4) diesel/gasoline engines 7 2005 Production Facilities in ASEAN Myanmar Vietnam Lao Cai Mandalay MYANMAR (BURMA) Vietnam Hong Kong Socson 2 4 Hanoi 8 Me L inh 1 LAOS K B Haikou Gulf of Tongking Hainan Yangon (Rangoon) Udon Thani M Hue g on ek Moulmein THAILAND Gulf of Martaban Da Nang Nakhon Ratchasima Bangkok S ou t h China Sea Qui Nhon CAMBODIA Gulf of Thailand Andaman Sea VIETNAM Phnom Penh Bien Hoa Ho Chi Minh City 7 3 5 6 Can Tho Palawan ■AUTOMOBILE PRODUCTION COMPANIES Automaker Company Products s Employees Capital Investment Headquarter’ Stake Established Production 1 Daihatsu Vietindo Daihatsu Automotive Corporation Hijet, Citivan, Terios 1995 581 units 132 US$ 12.3 million 26% 2 Hino Hino Motors Vietnam, Ltd. medium & heavy-duty trucks and buses 1996 661 units 48 US$ 8.11 million 51% 3 Isuzu Isuzu Vietnam Co., Ltd. N-series, Trooper, Hi-Lander 1995 2,799 units 4 Mazda Vietnam Motors Corporation Mazda3, Mazda6, Premacy 1991 697 units 5 Mitsubishi 6 Mitsubishi Fuso Vina Star Motors Corporation (VSM) Lancer, Pajero, Jolie, Grandis 1995 US$ 15 million 35% 634 US$ 13.35 million 0%(*1) 265 5,005 units 330 US$ 16 millon 0% 1,211 units Canter 25% 7 Suzuki Vietnam Suzuki Corp. Carry, Wagon R+, Vitara 1995 4,053 units 337 US$ 18.5 million 35% 8 Toyota Toyota Motor Vietnam Co., Ltd. Camry, Corolla, Hiace, Land Cruiser, Innova, Vios 1995 13,168 units 559 US$ 49.14 million 70% (*1) Technology Tie-up INDIA CHINA Myanmar Kunming (BURMA) Salween MYANMAR Nanning Lao Cai y Irrawadd Ha Noi Hai Phong LAOS Gulf of Tongking Luang Prabang Chiang Mai Vientiane Bay of Bengal 1 Yangon Moulmein Udon Thani Hue Da Nang g Ubon Ratchathani on ek THAILAND M Gulf of Martaban Tak Haikou Hainan ■AUTOMOBILE PRODUCTION COMPANY Automaker 1 Suzuki 8 Company Myanmar Suzuki Motor Co., Ltd. Products Carry, Wagon R+ Established 1998 Production 266 units s Employees Capital Investment Headquarter’ Stake 33 US$ 6.7 million 60% Steady Growth in Production in ASEAN There has been a steady growth in production by JAMA member companies and their local partners over the past eight years. Production of passenger cars, trucks and buses in ASEAN in 2005 totalled 2 million units including export units, marking close to a 16% increase over the previous year. 2,200,000 ASEAN Total 2,000,000 1,800,000 Units Produced 1,600,000 1,400,000 1,200,000 1,000,000 800,000 600,000 400,000 200,000 0 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Export Expansion in ASEAN Exports, including intra-ASEAN exports, registered the largest increase. Exports of motor vehicles produced in ASEAN by JAMA member companies and their local partners surged in 2005 to over 405,000 units, a 53.6% increase over the previous year. 450,000 400,000 350,000 Units Exported 300,000 250,000 200,000 150,000 100,000 50,000 0 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 9 JAMA's Activities in ASEAN Bilateral and Multilateral Economic Partnerships with ASEAN Countries Further progress was made in 2005 in the discussions and negotiations on economic partnership agreements (EPAs) between Japan and ASEAN countries. JAMA supports the establishment of EPAs to complement multilateral trade, enhance investment and market liberalization, and expand markets in the countries concerned. In 2004-2005 Japan reached basic agreements—also covering the automotive sector — on EPA creation with Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand. EPA negotiations were also launched with Indonesia and ASEAN itself. In addition to increasing market access between/among the countries involved, these agreements are expected to further enhance the competitiveness of those countries’ automotive industries and lay the groundwork for a win-win relationship for all. The 8th AMEICC WGAI Meeting The AMEICC (AEM-METI(*1) Economic and Industrial Cooperation Committee) Working Group on the Automobile Industry, or WGAI, was set up in 1998 and meets annually to examine and discuss automotive sector issues in the context of ASEAN economic and industrial cooperation. Its 8th meeting was held in May 2005 in Kuching (Malaysia) and featured a keynote address by JAMA Chairman Itaru Koeda, in which he emphasized that “speed” was a critical factor in automotive market integration in ASEAN to prevent it from being left behind by the worldwide automobile industry. Mr Koeda also stressed the need to expedite tariff reduction, mutual complementation and the removal of non-tariff barriers in the auto sector through EPAs. The meeting reported on and discussed the current status of harmonization of automotive technical regulations, fuel quality, the Experts Dispatch Program, cooperation initiatives for CMLV(*2) and other cooperation projects. (*1) ASEAN Economic Ministers-Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (Japan) Consultations (*2) Cambodia, Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam 10 The Experts Dispatch Program for ASEAN’s Auto-Supporting Industries The Experts Dispatch Program was launched in 2000 as an AMEICC-WGAI industrial cooperation initiative to dispatch Japanese automotive technical experts to Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines and Thailand to provide guidance to local parts suppliers in such areas as quality control and productivity enhancement. Positive feedback has led to the extension of the Experts Dispatch Program through September 2006 — that is, through the completion of Phase 3 of the program, during which, thanks to a JODC (Japan Overseas Development Corporation) scheme, local parts suppliers are receiving hands-on training in the total management of kaizen activities. The program has been enhanced by a greater number of visits to automakers’ and parts makers’ plant facilities and more active dialogue with top management at the companies involved. Trainees can thereby acquire not only technical skills but also problem-solving skills, all of which should help generate independent self-improvement activities in the individual countries concerned. The success of the Experts Dispatch Program raises further expectations for the increased global competitiveness of the automotive industry in ASEAN countries. The Experts Dispatch Program: Phase 1 (April 2001∼March 2003) and Phase 2 (October 2003∼September 2005) Indonesia Malaysia The Philippines Thailand Phase Number of Companies Visited (incl. multiple visits to a company) Number of Experts Dispatched (incl. 1 coordinator per country) 1 25 20 2 32 25 1 45 20 2 58 20 1 42 19 2 36 11 1 110 33 2 90 31 11 JAMA's Activities in ASEAN The JAMA-AAF Meeting At the 5th AAF/TC3(*3)-JAMA Meeting held in April 2005 in Singapore, the AAF/TC3 chairman announced that TC3 had been officially designated by the ASEAN Economic Ministers as one of the implementing bodies assigned the task of harmonizing ASEAN countries’ automotive fuel and safety standards on the basis of the UN/ECE Regulations. Also at that meeting, JAMA technical experts provided (1) guidelines for the adoption of the UN/ECE Regulations; (2) advice on certification procedures following the adoption of those regulations; (3) recommendations on EURO2 fuel specifications; and (4) suggestions concerning an appropriate stance on the use of bio-fuel. Furthermore, TC3 invited JAMA to draft a proposal for AAF fuel specifications based on EURO4 fuel specifications, to be presented at the 6th AAF/TC3-JAMA Meeting in 2006. (*3) ASEAN Automotive Federation/Technical Committee 3 The 10th Asian Regulation & Certification Experts (RACE) Meeting JAMA was the host of the 10th Asian RACE Meeting which took place in November 2005 in Kuala Lumpur, one day ahead of the JASIC/Asia Government and Industry Meeting also held there. In addition to the industry participants from India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam, the meeting saw the first-time-ever participation of the ASEAN Secretariat. Delegates from Thailand, Malaysia and India announced at the meeting that their respective countries would accede to the UN/ECE 1958 Agreement and/or the 1998 Global Agreement. JAMA experts highlighted the difficulties of harmonization activities in Asia and provided advice on the adoption of the UN/ECE Regulations from the standpoint of the 1958 Agreement. Participants concurred that there would be obstacles to technical standards harmonization in Asia if the UN/ECE Regulations were not adopted, and they concluded that such harmonization would be best served by close cooperation between the relevant government authorities (namely, the ministries in charge of the automotive sector and transport) and the national auto manufacturer associations. 12 Fuel Seminars To promote greater recognition of the fact that, even with engine upgrades, better air quality will not be achieved in ASEAN countries without improving automotive fuel quality, fuel seminars were held in the Philippines and Indonesia on 25 and 28 January 2005, respectively, co-organized by JAMA, the Japan Automobile Research Institute (JARI), METI, the Japan Petroleum Energy Center (JPEC) and local auto industry associations. Another fuel seminar was held in Vietnam on 31 January, co-organized by JAMA, JARI, the Vietnam Directorate for Standards and Quality (STAMEQ) and the Vietnam Automobile Manufacturers Association (VAMA). In those seminars JAMA fuel experts outlined for participants—in terms of fuel specifications, vehicle emissions performance, environmental impact and national policy — the background to Japan’s use of improved automotive fuels. They also explained the specific relationship between fuel quality and automotive emissions control technologies. The common conclusion at the seminars in the Philippines, Indonesia and Vietnam was that combined efforts on the part of government and industry would be crucial to improving fuel quality in those countries. Cooperation in the Organization of Motor Shows With ASEAN’s auto industry associations expanding their efforts in the organization of motor shows in the region, JAMA is extending its cooperation by sharing its organizational know-how based on long experience with the Tokyo Motor Show and by dispatching speakers to symposiums held in conjunction with those shows. JAMA contributed to such an event in April 2005 at the 26th Bangkok International Motor Show by arranging for a speaker from Intelligent Transport Systems Japan to talk about the application of ITS technology to road safety and transport demand management, in Japan and worldwide; and for a delegate from METI to discuss the provisions and enforcement of Japan’s automobile recycling law. JAMA also sent its own representative to the GAIKINDO (Association of Indonesian Automotive Industries) International Automotive Conference at its Auto Expo 2005 in Jakarta in July to speak about “leveraging strategies,” in which it was stressed that public and private sector cooperation—and also the cooperation of all road users—is necessary in order to achieve increased road safety and greater environmental protection and thus to ensure sustainable mobility. These various talks were intended to address some of the most urgent concerns in ASEAN’s automotive sector and promote a better understanding of the issues involved. 13 The History of Japanese Automakers in ASEAN 1996 1997 1998 1999 14 Daihatsu starts production of the Hijet at Vietindo Daihatsu Automotive Corporation, its joint venture company in Vietnam. Hino establishes Hino Motors Vietnam, Ltd. in Vietnam. Aggregate motorcycle production at Honda in both Indonesia and Thailand reaches 5 million units. Isuzu establishes Isuzu Motors Asia Ltd. in Singapore as its regional administration and support center. Nissan Diesel establishes a joint venture company for truck and bus production with P. T. Astra Nissan Diesel Indonesia (Jakarta) in Indonesia. Suzuki starts automobile and motorcycle production at Vietnam Suzuki Corp. Ltd. in Vietnam. Toyota starts production at Toyota Motors Vietnam Co., Ltd. in Vietnam. Aggregate automobile production at MMC Sittipol Co., Ltd. of Mitsubishi in Thailand reaches 1 million units. Nissan opens Siam Nissan Casting Co., Ltd., its production base for cast engine parts in Thailand. Nissan starts production at a new factory of Nissan Motor Philippines Inc. (NMPI), its production and sales base. Daihatsu increases capital investment in P. T. Astra Daihatsu Motor in Indonesia. Honda starts exporting the Thai-made Accord following the City in 1997. Mitsubishi constructs a new plant of Asian Transmission Corporation in the Philippines. Suzuki concludes a joint venture contract for motorcycle and automobile production with Myanmar Suzuki Co., Ltd. Toyota starts exporting its models made in Thailand. Hino integrates its two affiliates in Thailand, Thai Hino Motor Sales, Ltd. and Thai Hino Industry Co., Ltd., into the newly created Hino Motors (Thailand) Ltd., investing capital of 713 million bahts. Independent automobile distributorship in the Philippines becomes Suzuki Philippines Inc., a wholly-owned local subsidiary selling passenger cars and commercial vehicles. 2001 2002 2003 Daihatsu establishes Perodua Auto Corporation Sdn. Bhd. in Malaysia. Honda achieves an aggregate production level of 10 million units for motorcycles, automobiles and power equipment in Thailand. Nissan increases capital investment in P. T. Ismac Nissan Manufacturing in Indonesia, with a name change to P. T. Nissan Motor Indonesia (NMI), and integrated production and sales operations. Subaru starts sales of its models through GM Auto World in the Philippines. Subaru starts sales of its models through GM Auto World in Indonesia. Toyota establishes Toyota Motor Asia Pacific Pte. Ltd. in Singapore. Daihatsu increases capital investment in P. T. Astra Daihatsu Motor in Indonesia. Honda begins exporting the Thai-made Fit Aria to Japan. Honda constructs a new plant for automobile production in the Karawang district in Indonesia. Suzuki holds a capital majority in P. T. Indomobil Suzuki International in Indonesia. Hino (Indonesia) establishes a new sales company, P. T. Hino Motors Sales Indonesia, in April to take over sales operations from P. T. Hino Indonesia Manufacturing, which previously handled both manufacturing and sales and which then becomes, also in April, P. T. Hino Motors Manufacturing Indonesia (HMMI). Hino (Thailand) establishes a new company, Hino Motor Manufacturing (Thailand) Ltd. (HMMT), in June as a separate manufacturing division of Hino Motors Thailand Ltd. (HMT), which previously handled manufacturing and sales. In July, HMT becomes Hino Motors Sales (Thailand) Ltd. (HMST). Hino obtains permission under the AICO scheme in September to begin a mutual industrial complementation arrangement between Thailand and Malaysia, as a result of the abolition of the nationalized production law in Thailand in January 2001. Honda opens a new automobile production factory in Pegoh, Malaysia. This factory also produces and exports constant velocity joints to Asia. 2003 2004 Honda opens a new automobile production factory in Karawang, Indonesia and starts exporting its Indonesian-made Stream to Thailand. Honda opens a new manual transmission plant in the Philippines and expands its exports to Europe and North America. Honda opens a hi-tech automatic transmission plant in Indonesia and starts exporting to ASEAN countries and Europe. Mitsubishi's production and sales arm in Thailand, MMC Sittipol Co., Ltd., becomes Mitsubishi Motors (Thailand) Co., Ltd. in order to reinforce sales and marketing through a common company name. Mitsubishi also posts aggregate exports of over 500,000 units for one-ton pickup trucks. Suzuki establishes Suzuki Automobile (Thailand) Co., Ltd. as a distributor of automobiles in Thailand. Toyota-Astra Motor (TAM) is split into two companies to handle sales and manufacturing (TAM for sales, TMMIN for manufacturing). Toyota establishes Toyota Technical Center Asia Pacific Thailand Co. Ltd. (TTCAP-TH) in Thailand as a technical development center in Asia. Honda opens a new Automobile Technical Training Center in Thailand in August. The Center undertakes the training of not only automobile sales and service personnel in Thailand, but also ASEAN instructors. It is also open to 3rd party users such as vocational schools. A new production and administration company, Isuzu Motors Co., (Thailand) Ltd., is established in Thailand in September 2004 by the combination of its local administration company, Isuzu (Thailand) Co., Ltd., and its local production company, Isuzu Motors Co., (Thailand) Ltd. At the moment of the establishment, Isuzu Motors Co., (Thailand) Ltd. receives an additional amount of 7 billion bahts to its capital, which becomes 8.5 billion bahts. Mitsubishi annual auto export total to Thailand surpasses 80,000 units, setting new record high. Mitsubishi announces the new automobile developed independently by PROTON at Malaysia in February, and starts sales of it in April. 2004 2005 Mitsubishi spins off local operation in 2004, establishing Mitsubishi Fuso Truck (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (MFTT) as truck/bus specialized production and sales company in Thailand. Nissan invests more than 10 billion bahts in Siam Nissan Automobile Co., Ltd. The number of Siam Nissan's employees is expected to at least double by 2008 from about 2,000 at present. Toyota starts exporting the Indonesia-made Avanza to Thailand. Toyota launches IMV (Innovative International Multi-purpose Vehicle) project by starting production of pick-up trucks and SUVs in Thailand and mini-vans in Indonesia. Honda announces to build a new automobile manufacturing facility within the current motorcycle plant site to begin its automobile business in Vietnam after the middle of 2006. Mitsubishi's new and exclusive sales network in Malaysia; Mitsubishi Motors Malaysia Sdn. Bhd., a joint venture company between Mitsubishi Corporation and Edaran Otomobil Nasional Berhad (EON), is established in March 2005, and starts its sales in July 2005. Mitsubishi (Thailand) announces that its automobile export exceeded 700,000 units by March. Mitsubishi Fuso transfers its truck and bus operation in Malaysia to DaimlerChrysler Malaysia (DCM) from January 1, 2005. Nissan newly installs Upsetter line (two lines in total) in Thailand. Toyota starts production of IMV models in the Philippines in February and Malaysia in March. Toyota announces that its production capacity increases up to approximately 550,000 vehicles annually and construction of a new plant in Thailand in April. Toyota announces that its Karawang plant production capacity increases up to approximately 100,000 vehicles annually in Indonesia in April. 15 Head Office Jidosha Kaikan, Shiba Daimon 1-chome, Minato-ku Tokyo, 105-0012 Japan TEL: +81-3-5405-6126 FAX: +81-3-5405-6136 URL:http://www.jama.or.jp/ Singapore Representative Office 143 Cecil Street #09-03/04 GB Bldg. 9F Singapore 069542 TEL: +65-6221-5057 FAX: +65-6221-5072 North American Office 1050 17th Street, N.W., Suite 410 Washington, D.C. 20036, U.S.A. TEL: +1-202-296-8537 FAX: +1-202-872-1212 URL: http://www.jama.org/ European Office Avenue Louise 287 box 9, 1050 Brussels, Belgium TEL: +32-2-639-1430 FAX: +32-2-647-5754 Beijing Office Unit 1001B, Level 10, China World Tower 2 No.1 Jian Guo Men Wai Avenue Beijing, 100004 China TEL: +86-10-6505-0030 FAX: +86-10-6505-5856
Similar documents
Hand in Hand between ASEAN and Japan
 chassis, Iveco MaxiBus, Mitsubishi Fuso
(Commercial Vehicle)
chassis, Iveco MaxiBus, Mitsubishi Fuso
(Commercial Vehicle)




 MYANMAR
(BURMA)
MYANMAR
(BURMA)




 Banjarmasin
Banjarmasin
