上名川演習林
Transcription
上名川演習林
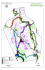
Yamagata University Research Forest Guide Ostrich fern (Mateuccia struthipyeris) Rose of winter(Camellia japonica var. decumbens) Survey of a secondary beech forest Sketch of Beech (Fagus crenata) Fuki(Patasites japonica) Snowcat during winter in YURF Watershed Conservation Laboratory, Yamagata, Field Science Center, Faculty of Agriculture Introduction The Laboratory of Watershed Preservation of the Yamagata Field Science Center attached to the Faculty of Agriculture of Yamagata University with the YU Research Forest (YURF) and the Experimental Research Site for Biodiversity, focuses education and research on building environment-friendly sustainable forest management that includes forest restoration and conservation. YURF is located 26 km south of the Faculty of Agriculture and it is characterized by very steep slopes as well as heavy snowfall in the Asahi Mountains. Almost 80% of the 753 ha of YURF territory is occupied by natural beech forests. The Laboratory of Watershed Preservation carries long-term monitoring of water and energy cycles of the interaction of the forest-ecosystem and the heavy snow environment. Moreover, YURF and the Experimental Farm are located in the same watershed and share the same geographical and locally typical agriculture and silviculture characteristics. In order to farther promote joint activities, the Eco-Agriculture Laboratory and the corresponding Department collaborate and made the land arable in the forest by the slash and burn method to grow Atsumi Turnip. The application of silviculture and agriculture as a single unit is the teaching material for what is called Agro-forestry. Moreover, in order to give back to the community the results of Education and Research, we conduct events that target the general public. The Experimental Research Site of Biodiversity is located in Tsuruoka and it is used for students’ experiments and nursery practices. History Kaminagawa YURF May 1949 As part of the establishment of the Faculty of Agriculture in Yamagata University, 411 m2 of state owned forest and 12 m2 of constructed building is borrowed from the Prefecture from a total of 753.05ha All the forest is received from Yamagata Prefecture New buildings were made in an area of 79 m2 for storing machinery and a room for drying clothes. Construction of a building in a 709.39 m2 for the student’s dormitory. As part of the formation of Yamagata Field Science Center, the name was changed to Watershed Preservation Laboratory (Kaminagawa YURF). Remodeling of the administration building and the student’s rooms. April 1953 November 1967 October 1982 July 2006 November 2007 Experimental Research Site for Biodiversity Conservation April 1953 March 1970 March 1981 October 1982 Part of the student’s dormitory area was taken to establish a nursery. Building for compost of 23 m2. Construction of a 137.60 m2 for administration. The name for the Wakabamachi nursery is changed into the Experimental research site for biodiversity conservation. Departments Department Watershed Preservation Lab. KaminagawaYURF Experimental Research Site for Biodiversity Conservation Support team Address 〒997-8555 Tsuruoka, Wakabamachi 1-23 〒997-0405Tsuruoka, Kaminagawa Azagasadagawa 〒997-8555 Tsuruoka, Wakabamachi 12-5 〒997-0369 Tsuruoka, Ooazatakasakakomachi 5-3 Telephone 0235-28-2961 0235-53-2755 0235-24-4060 0235-24-2278 Personnel Section Watershed Preservation Lab. Kaminagawa YURF Support team Faculty 1 Office Technician 3 2 Total 1 3 2 Location The Kaminagawa YURF is located at the Echigo Range at the northern end of the Asahi Mountains and occupies a part of the Wasada River watershed tributary of the Bonji River. The shape of the YURF has almost a rectangular shape. It has an extension from north to south of approximately 2.1 km and an extension east to west of approximately 3.5 km, with a total perimeter of 13.2 km and a total area of 753 ha. YURF is crossed almost exactly at the middle by the Wasada River. On the southern border YURF is in contact with the National forest under the Administration of the Japanese Forest Agency and on the North, West and East side it is surrounded by Tsuruoka city owned forest. The building for the administration and the students’ dormitory is located almost in the central point of the YURF. It is 26 km away south of the Faculty of Agriculture or 45 minutes by car. On the other hand, the Experimental Research site for Biodiversity Conservation is 10 minutes walk from the Faculty of Agriculture and has an area of approximately 0.64 ha. Climate YURF is located in northeastern Japan on the Japan Sea side and has mountainous climatic characteristics with an average annual air temperature of 13.4℃, annual precipitation of about 2,500mm and annual average maximum snow depth of approximately 4.0 m. Geographical features The bedrock of YURF is amphibolites Tertiary granite, mainly from pyroxene andesite. A glay soil layer as well as can be seen in some of the terrain at the plateau at around 800m.a.s.l. The altitude ranges between 200 to 840 m in a basically mountainous area with very steep slopes of almost 30 degree. Most of the forest at YURF distribute in these slopes. Trees and vegetation YURF is covered extensively by beech forests, which is representative of the cold temperate area and mixed-forests of Quercus 、 Japanese big-leaf Magnolia 、 Japanese maple 、 Korean whitebeam and understory vegetation of Camellia Japonica、Himeaoki、Ezoyuzuriha、Haiinugaya that are typical of the Japan Sea Coast. One part of the broadleaf forests was replaced by needle-leaf species such as Cedar, Cypress, Red pine and Larch. At an altitude of about 800 m.a.s.l. in the Yachibaba bogs there are typical plants such as Asian Skunk Cabbage, Numagaya, Yachizgaran, Round-leaved sundew、Iwashoubu、 Onishiogas, etc. Beech in Spring Mizubashi at the Yachibaba bog Education Field Science Education in YURF is attached to the Faculty of Agriculture mainly for undergraduate and graduate students’s research but actually targets students from all the Faculties of the Universities. The main subjects taught at YURF are: ●Techniques of Field Sciences ●Yamagata Field Science II ●Freshmen Summer Seminar ●Approach to the Science of Environmental Biology ●Field Science Seminar III ●Watershed Preservation Course (Joint Faculties) ●Watershed Preservation Seminar ●Bio-environment Experimental Seminar ●Snow in Mountains Field Seminar ( Joint Faculties )●Forest Snow and Ice Science ●Earth Environmental Experimental Seminar ●Natural Environment Research Experimental Seminar ●River Environment Research Experimental Seminar ●Forest Ecology Experimental Seminar I ●Forest Survey Field Seminar●Forest Resources Use Experimental Seminar ●Forest Ecology Experimental Seminar II. Research We use the forest to write undergraduate, master and doctor students research thesis and for Education and Research by Professors of Yamagata University and other Universities as joint researches. The main topics of research are: ●Interaction of forest dynamics and snow behavior. ●Study on transpiration from Cedar and larch trees. ●Change of leaves in poor crop years and the following beech mast year. ●Effects of seed weight and germination time on beech growth and survival. ●Radiation level and the relationship between the forest canopy closure and density regulation in a secondary beech forest ●The effect of acid rain and acid snow on the forest. ●Variability of aquatic insect in Wasada River. ●Research about grazing in the forest. ●Research about slash and burn practices. ●Ecological research on tree root systems. ●Conservation study of the Yachi bog. ●Development of Agro-forestry technology for Satoyama practices Enjoying and learning the Science of snow (Yamagata Field Science II) Measuring snow depth cross-section (Forest Snow Field Seminar) Wood bended by snow and used for furniture (Watershed Preservation Field Seminar) Yachida Giant Trees Survey (Water Shed Preservation Excursion) Community participation We implement a program in which school children and the community in general experience the forest and learn about its environment in the YURF Forest School-Activities during the four season Forest school members and forest master craftsmen Agro-forestry Traditional slash and burnt practices in Shonai region combine forestry, agriculture, grazing and husbandry in what is called Agro-forestry. ① Fire is set in an old cedar forest clear-cut ③Cultivated turnip with no fertilizer or pesticide ②Turnip seedling right after the fire ④Grazing in Cedar forests Four seasons at YURF Snow accumulation Planting Japanese cedar Setting fire for research Beech forest in summer Snow removal from the building roof Cutting weed at the cedar plantation One day after burning Yachihaba bogs in autumn Activities at the YURF Making wood figures with the chainsaw Grazing in the forest Making a biotope Trying to reach the YURF in winter Making firewood Planting mushrooms in beech stems Making an artificial pond The snowcat gives better results Map of roads in YURF 北 Community-owned forest Entrance Mountain God Daitokusawa road Ashisawa road Shakuhira bridge Larch road Yachihaba bogs Building State-owned forest Distribution of tree species Japanese Cedar Oak Deciduous Forest Beech Beech