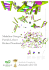Sample Lysis and DNA Separation in Single Tube Assemblies Abstract
Transcription
Sample Lysis and DNA Separation in Single Tube Assemblies Abstract
Sample Lysis and DNA Separation in Single Tube Assemblies for Accurate Forensic Profiling Dr. Helge Schnerr – Biotype Diagnostic GmbH, Moritzburger Weg 67, 01109 Dresden, Germany Abstract The importance to improve quantity and quality of DNA isolated from forensic samples is without controversy. High quality extraction of genomic DNA, as the first step of DNA profiling, is most critical for successful downstream Short Tandem Repeat (STR) analysis. Therefore, disruption of cellular structures and separation of the soluble DNA fraction from cell debris needs to be optimized. Overall efficiency and yield of the particle free DNA lysate will be improved by carrying out the lysis directly in a single tube assembly concomitantly allowing subsequent quantitative lysate recovery. Sampletype i-sep® DL Sampletype i-sep® SQ Unique to the DL version is the gradual DNA extraction required for differential lysis of mixed specimens. Moreover, an immunological pretest for semen can be carried out using the identical sample. The single tube assembly thus joins maximum comfort with most accurate performance. The SQ extraction systems mediates economic savings, reduces the risk for cross contamination while improving the yield and quality of DNA isolated from forensic samples such as swabs. It allows simple and fast separation of substrate from lysate in an all-in-one system. Thus, manual lysate and substrate transfer steps are eliminated, which significantly rationalizes the work flow as exemplarily shown below: Experiment: Differential lysis was performed under mild conditions to separate the female DNA and harsher lysis conditions that break open the spermatozoa as depicted below: The DNA lysates were further purified and an autosomal STR profile of both the victim and the perpetrator were generated using the particular volumes of DNA-eluate. Experiment: To demonstrate flexibility of the system in terms of lysis conditions and required reagents a variety of lysis protocols were tested (data not shown). Further, a rapid and inexpensive alternative to DNA isolation for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification from blood was developed. A volume of 36 µl 1 M Tris, pH 7.4 were added to the collection tube. A filter column containing the sample (dried blood on textile 4 x 4 mm) was inserted. A volume of 200 µl 0.1 N NaOH was added and incubated on a shaker (550 rpm, 5 min). The assembly was centrifuged at 13.400 rpm for 1 min. The resulting lysate was mixed well and 5 µl were used directly in the PCR. 6 µl Conventional Extraction methode 17 µl Sampletype i-sep® SQ 6 min DNA-ExpressIsolation 4 µl Sampletype i-sep® DL 1 µl *Data provided by State Office of Criminal Investigation Saxony Results: High quality yields of extracted DNA optimized down-stream profiling. Thereby, simple handling allowed time savings and higher throughput. Together, the DL-version has clear potential to reliably improve crime solution rates and to speed up analysis of backlogged crime samples. *Data provided by State Office of Criminal Investigation Saxony Results: High quality results, comparable to conventionally determined results, were achieved using a 6-min-DNA-Express-Isolation. So, Sampletype i-sep® SQ replaces present approaches requiring DNA purification prior to PCR by combining incubation and separation with high quality performance. The simple protocol is fast, easy to perform, cost-effective, and consequently ideal for large sample numbers in the routine. Furthermore, the Sampletype approach avoids anyway switching to another tube. Thus eliminating the two-man rule during sample preparation saving resources and minimizing the risk of cross contamination and sample transposition events significantly. Conclusion Sampletype i-sep® extraction systems dramatically streamline the off-line lysis portion of the extraction method. Improvements of overall efficiency, in particular maximizing the performance of the early steps of the extraction method has been demonstrated to achieve optimal genotyping results. Ethylene oxide (EO) sterilization, according to the recommendations of the German Federal Criminal Police offices, has been applied to guarantee DNA-free products. In addition, Sampletype i-sep® DL can be rated as an improved methodology to overcome the often claimed difficulties in differential extraction, thus, has the potential to work off backlogs of rape kits estimated at ~500.000 alone in the US1. Consecutive fractions of several lysates are prepared by simply centrifugation; even allowing for an immunological pre-test using the identical sample. References 1 Norris JV, Manning K, Linke SJ, Ferrance JP, Landers JP, Expedited, Chemically Enhanced Sperm Cell Recovery from Cotton Swabs for Rape Kit Analysis. J. Forensic Sci., 52, 800-805 (2007). Scan or Visit www.biotype.de