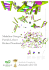Completely automated ambient temperature biobanking. Workflow for sample collection, transport
Transcription
Completely automated ambient temperature biobanking. Workflow for sample collection, transport
Completely automated ambient temperature biobanking. Workflow for sample collection, transport and storage of human blood samples for molecular RNA and DNA diagnostics. Vasco Liberal, Angela Stassinopoulos, Scott Whitney, Steven Wilkinson, Winnie Huang, Rolf Muller and Judy Muller-Cohn Biomatrica, Inc., 5627 Oberlin Drive, Suite 120, San Diego, CA 92121 Results Abstract Analysis of genomes and gene expression profiles are being increasingly used for diagnosis and monitoring of disease, and require reliable nucleic acid preservation during sample collection and shipment. Transcription profiles can change rapidly after sample collection, potentially affecting interpretation of gene expression and ultimately dictating inadequate treatment. Biomatrica’s RNAgard® Blood Tube is a device for whole blood collection, which stabilizes both the RNA and DNA in blood cells and allows for ambient temperature blood sample handling and storage. Coupled with robust purification methods for both nucleic acids, it provides a complete solution for blood collection and storage, yielding both high quantity and quality of RNA and DNA. RNA isolation can be performed with multiple automated platforms, allowing ease and flexibility in the workflow and excellent results for low to high throughput sample processing. Moreover, the RNAgard Blood Tube allows for the isolation of both DNA and RNA from the same patient sample, simplifying logistics, especially when large sample sets are required. Isolation of RNA and DNA from the same sample is ideal, since the use of separate samples could introduce operation errors and variation of results. We have therefore developed an automated workflow for sequential RNA and DNA purification, using the MagNA Pure System (Roche). Biomatrica’s ambient temperature nucleic acid preservation technology, coupled with automated purification, can provide accurate gene expression profiles, proving highly valuable for improved biomedical research and potential patient treatment. Collection Transport Process Archive RNA Isolation using the automated MagNA Pure System Figure 1: High yields of pure RNA from blood specimens in RNAgard Blood Tubes using the MagNA Pure Compact System. Blood from two human donors was collected in RNAgard Blood Tubes and stored at ambient temperature for 14 days. RNA was isolated from triplicate blood specimens per donor on the MagNA Pure System, and was analyzed for RNA yield (A) and RNA purity (A260/A280) (B) . DNA Isolation using the automated MagNA Pure System Figure 4: High integrity and yield of genomic DNA isolated by the MagNA Pure System from blood stored in RNAgard Blood Tubes. Triplicate blood samples per donor from two donors was analyzed at Day 0 and after 14 days of ambient temperature storage. The DNAcontaining supernatant recovered after RNA pelleting (see methods) was processed for DNA isolation. DNA integrity was assessed by agarose gel electrophoresis (A) and yield was measured by UV specrophotometry (B). Distribute Materials and Methods Blood collection and storage: Human blood from two healthy donors was collected in RNAgard Blood Tubes. Nucleic acid isolation was performed immediately upon blood arrival in the laboratory (Day 0). The remaining blood tubes were stored at ambient room temperature for 14 days before processing. Automated nucleic acid isolation: RNA isolation: Three RNAgard Blood Tubes were processed for nucleic acid isolation per donor at each time point. RNA was pelleted in blood samples by the addition of BioMaxi™ Precipitation Buffer followed by centrifugation according to the standard procedure for the RNAgard Blood System. The DNA-containing supernatant was saved for separate DNA purification. The RNAcontaining pellet was resuspended in 200 µL of lysis buffer from the MagNA Pure Compact RNA Isolation Kit, and RNA was purified using the MagNA Pure Compact System (Roche Applied Sciences). DNA isolation: The DNA-containing supernatant was processed for DNA isolation on the MagNA Pure Compact instrument with the MagNA Pure Compact Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit I. RNA analysis: RNA integrity was assessed by agarose gel electrophoresis and Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. Total RNA yield and purity were measured by UV spectrophotometry. Gene expression levels after 14 days of blood storage of c-Fos and IL-1β were normalized to 18s rRNA and quantified by the ΔΔCt method relative to transcript levels at Day 0. Genomic DNA contamination levels were quantified by qPCR amplification of an RNaseP amplicon. DNA analysis: DNA integrity was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis and by long-range PCR amplification of a 7.5 kbp region from the β-globin gene followed by electrophoresis. DNA yield and purity were quantified by UV spectrophotometry. Figure 2: High integrity of RNA isolated from RNAgard Blood Tubes after 14 days of ambient temperature storage. The integrity of RNA recovered on the MagNA Pure System from triplicate blood specimens per donor was assessed using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. Average RIN values (A), gel-like images (B) and electropherogram data (C) are shown. Figure 5: Spectrophotometric analysis of genomic DNA purity and assessment of DNA integrity by long-range PCR. The purity of DNA isolated from triplicate RNAgard Blood Tube specimens per donor was quantified by UV spectrophotometry (A). DNA integrity from the 14 day old RNAgard Blood samples was assessed by long-range PCR amplification of a 7.5 kbp region of the β-globin gene and compared to amplification from fresh blood DNA. Summary Ambient temperature blood storage automated nucleic acid isolation: coupled with • RNA and DNA stabilized in human blood for 14 days at ambient temperature in RNAgard Blood Tubes Figure 3: Transcript stability and low genomic DNA content in RNA samples isolated from RNAgard Blood Tubes. Transcript stability after 14 days of ambient temperature blood storage was verified by comparison to c-Fos and IL-1β levels at the time of blood collection (time 0). Transcript levels were quantified by RT-qPCR using 18s rRNA as the reference gene (A). Genomic DNA content in purified RNA samples was quantified by qPCR amplification of an RNaseP target as a function of input nucleic acid. • Automated RNA and DNA isolation from RNAgard Blood Tubes (Biomatrica) using the MagNA Pure System (Roche Applied Sciences) o RNA • Stable transcription profile • Yield > 3 µg/ tube • Superior quality and purity o DNA • Excellent purity • Highly intact • Yield > 10 µg/ mL blood