Common causes of dysphagia Mechanical Oesophageal stricture Oesophageal spasm
Transcription
Common causes of dysphagia Mechanical Oesophageal stricture Oesophageal spasm
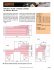
Table 7.3.1 Common causes of dysphagia Mechanical Neurological Psychological Oesophageal stricture Oesophageal spasm Cancers in the head, neck and oesophageal areas Cancer treatment including radiotherapy/ surgery to head and neck area Pharyngeal pouch Injury or surgery to the tongue, lips, mouth or jaw Severe infections of the mouth or throat, e.g. oral thrush or ulcers Postural problems, e.g. severe kyphosis (curvature of the spine) Stroke Parkinson’s disease Motor neurone disease Head injury Multiple sclerosis Cerebral palsy Dementia Huntington’s disease Drug induced (psychotropic drugs) Globus hystericus Severe anxiety Severe depression Table 7.3.2 Disruption of the normal swallowing process Stage of the normal swallow Affected by Consequences Preparatory stage Reduced range of movement of facial muscles, lips, tongue and jaw Loss of sight, smell and/or taste Reduced range of movement of facial muscles, lips, tongue and jaw, and lack of saliva Postural problems Difficulty in getting food/liquid into the mouth Difficulty in sealing the mouth Reduced saliva production Difficulty in mastication Difficulty in forming a food bolus Difficulty in controlling a food bolus Difficulty in swallowing a food bolus Inability to swallow safely Food fails to move into the stomach Aspiration after the swallow Oral stage Pharyngeal stage Oesophageal phase Absence of swallow reflex Impaired peristalsis or obstruction Manual of Dietetic Practice, Fifth Edition. Edited by Joan Gandy. © 2014 The British Dietetic Association. Published 2014 by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Companion Website: www.manualofdieteticpractice.com Table 7.3.3 Prethickened commercial proprietary prescribable products Product (manufacturer) Thickened desserts Thickened drinks Ensure Plus Crème (Abbott Nutrition) Forticreme Complete (Nutricia Advanced Medical Nutrition) Fortisip Fruit Dessert (Nutricia Advanced Medical Nutrition) Fresubin Creme (Fresenius Kabi Ltd) Fresubin Thickened Stage 1 (Fresenius Kabi Ltd) Fresubin Thickened Stage 2 (Fresenius Kabi Ltd) Nutilis Complete Stage 1 (Nutricia Advanced Medical Nutrition) Resource Thickened Drink (Nestles Healthcare Nutrition) Resource Dessert Energy (Nestles Healthcare Nutrition) Resource Dessert Fruit (Nestles Healthcare Nutrition) Thick and Easy Thickened Juice Drink (Fresenius Kabi Ltd) SLO Cold Juice Drinks, Hot Chocolate, White Coffee (SLO Drinks Ltd) NB: The above products are not normally suitable for infants and young children. Thickeners based on carob seed flour such as Carobel instant powder (Cow & Gate) are used to thicken infant feeds for the treatment of recurrent vomiting. They are not suitable for the management of dysphagia. Full composition details of these products and prescribing indications can be found in the British National Formulary or the Monthly Index of Medical Specialties (MIMS) or obtained directly from the manufacturers. Table 7.3.4 High risk foods in dysphagia [modified from Joint Working Party of the British Dietetic Association and Royal College of Speech and Language Therapists (2002, reviewed 2009) and Dietitians Association of Australia and The Speech Pathology Association of Australia Ltd (2007)] Food types Examples Chewy foods Chewy sweets and toffees Marshmallows Chew bars, breakfast bars Chewing gum Chewy or crispy meat, e.g. crispy duck, bacon Cooked hard cheese, e.g. cheddar Bread crusts, pie crusts Crumble Dry biscuits/cakes Toast Flaky pastry Dry biscuits Crisps, popcorn Lettuce, cucumber, uncooked spinach leaves Boiled and hard sweets and toffees Nuts and seeds Raw vegetables Sweetcorn Granary bread, bread with grains and seeds Cereals which do not blend with milk, such as muesli Mince with thin gravy Soup with lumps, e.g. minestrone Pineapple, runner beans, celery, rhubarb Steak Broad, baked, soya and black eyed beans, peas, grapes, sweetcorn, apple with peel Crumbly items Crunchy foods Floppy texture Hard foods Husk Mixed consistency foods Stringy, fibrous texture Vegetable and fruit skins (including bean skins)