The Great Barrier Reef
Transcription
The Great Barrier Reef
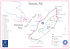
By: Ben Litwiller Intro. http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/place s/parks-and-nature-places/oceans/oceansbarrier-reef/ Location The great barrier reef is located out the northeast shores of Australia. Topography largest extent of coral reefs on Earth geographic range (24°30'N to10°41'S, 145°00' to 154°00'E) extends for more than 2000 kilometres within the Coral Sea off the eastern coast of Australia. Climate Climate Climate Climate Plants Mangroves make up the third type of plant growing near reefs More than 50 species of mangroves exist in the world. Florida's boasts about 469,000 acres found along the state's southern coast. Plants Of some 60 species of seagrass around the world, there are 30 in Australia and 15 in Queensland waters. *Seagrasses are different to seaweeds and algae *true roots and are the only flowering plants in the sea. Starfish in seagrass. *They are important food for turtles and dugongs. Plants 500 species of seaweed or marine algae live on the Great Barrier Reef *Most seaweeds are not poisonous to humans but a few, such as Caulerpa Plants Blue-green algae are more appropriately known as cyanobacteria originally thought to be a type of algae bacteria form green tufts on the reef which forms sometimes forms blooms in tropical waters. Plants Brown algae contain an extra pigment abundant in cooler climates a few species can be very common in summer on inshore Plants Golden algae are concerned about extensive blooms of seabed algae known as 'golden noodle algae Scientists have identified the bloom-forming alga as Chrysocystis fragilis has been found at Palau, Pohnpei and Hawaii. Endangered Animals Whales and dolphins Dugong Marine turtles get tangled up in fishing lines Animals 30 species of whales, dolphins and porpoises live in, or visit Great Barrier Reef waters *Visit the Reef every year in June and July. *They feed by straining tiny plankton and krill Dwarf minke whale. Animals Some of the largest populations of dugongs in the world live on the Great Barrier Reef *Dugongs grow to about 3m long *Can weigh 400 kg *live to 70 years old. Dugongs. *Dugongs have a single calf when they are between 6-17 years old Animals Over 200 species of birds (including 40 species of seabirds) live on the Great Barrier Reef *White-breasted sea eagles live on the coast and islands. *The Roseate tern migrates as far as Japan. White-breasted sea eagle. Animals Six breeding species of sea turtles live on the Great Barrier Reef *temperature of the sand determines the sex of the young turtles. *Cooler sand produces male turtles Green turtle hatchling. Measuring a Loggerhead turtle. *warmer sand produces females. Animals 14 species of sea snakes live on the Great Barrier Reef *evolved in the sea about 135 million years ago. *Sea snakes have to come to the surface to breathe Seasnake. *but can spend up to 2 hours underwater between breaths. More Animals 1500 species of fish live on the Great Barrier Reef *baby anemone fish can swim at 9.5 body lengths per second *The oldest fish on the Great Barrier Reef would be a red bass Clown anemone fish. Coral trout. Strange Animals 5,000 species of molluscs live on the Great Barrier Reef *Giant clams can grow to be more than 1 metre long *can be at least 70 years old. *They are the largest bivalve mollusc Giant clam. *Nudibranchs are a type of sea snail *Adult nudibranchs have a multi-coloured mantle instead of a shell. Nudibranch. People People can go snorkeling, diving, helicopter rides and cruises NO HURLIN ON THE SHELL DUDE People Great Barrier Reef contributes $6.4 billion a year from the tours employs more than 60,000 people. The interconnected reef system faces increasing pressure from climate change Jobs for people Aquariums Visitor service officer Marine Biologists Fishermen Tour Guides Unique Features the clownfish can actually help the sea anemones to breathe and can help them to aerate themselves Sea anemones gives the clownfish a place to live in exchange http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/coralreefs There are more symbiotic relationships similar to this found in the G.B.R. Relationships Commensalism the pearlfish uses the sea cucumber for a hide-out from predators lives in the sea cucumber’s anus Mutualism orange coral crab lives in and feeds off of the coral coral benefits as the resident crab cleans it and protects it Parasitism Sea spider gains food and nutrients from coral this relationship bleaches the coral Coral Attached to the ocean floor Waste produces products for photosynthesis for the algae Algae produces products need for the coral to grow Is home for most animals in the reef Environmental concerns lost more than half its coral cover in the past 27 years. Experts say storms, starfish and bleaching linked to climate change are to blame. Environmental concerns global warming overuse from tourism Fishing farming development on the coast and pollution both in the water and on the land. Before After Solving the problems * 30-50% of reefs to be set aside as "no take" or no fishing zones for long term protection * larger fines for fishing offenses * greater use of technology to enforce no fishing zones. Conclusion Beautiful place Cool animals All around fun place to go on vaction. Food web of the G.B.R. =P =P.C. =S.C. =T.C. 5 questions What are the four endangered species I minced in the P.P.? What can people do when visiting the reef? What is the biggest problem with keeping the reef healthy? What is the olds fish in the G.B.R.? How many speices of sea snakes are there? The websites http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Barrier_Reef http://www.cairns-greatbarrierreef.org.au/media/6481/diving_experiencecairns_great_barrier_reef.jpg http://www.deepreef.org/publications/peer-review/87-topography-gbr.html http://www.reef.crc.org.au/discover/plantsanimals/facts_plantanimal.htm http://wwf.panda.org/about_our_earth/about_freshwater/rivers/irbm/cases/great_barrier_reef_cas e_study/ http://www.environment.gov.au/topics/environment-protection/strategic-assessments/greatbarrier-reef http://cdn.greatbarrierreef.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2012/10/Great-Barrier-Reef-Food-Web-Diagram1.jpg http://www.oceanwideimages.com/images/8302/large/mangrove-jack-24M1844-12.jpg http://traveltips.usatoday.com/plants-live-coral-reefs-61384.html http://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/education-and-outreach/additional/science-focus/images/coral_reef_algae.jpg http://www.reef.crc.org.au/discover/plantsanimals/algae/ http://tolweb.org/tree/ToLimages/kelpy3.250a.jpg http://www.conservenature.org/learn_about_wildlife/great_barrier_reef/commensalism.htm http://switchboard.nrdc.org/blogs/fbeinecke/Healthy.coral.reef.No.Title.jpg http://awsassets.wwf.org.au/img/mo_corals_anthias_fish_fiji_808x236_4919.jpg