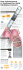GentleCath Intermittent Catheters Designed to reduce tissue deformation ™
Transcription
GentleCath Intermittent Catheters Designed to reduce tissue deformation ™
TM INTERMITTENT URINARY CATHETER GentleCath™ Intermittent Catheters Designed to reduce tissue deformation Intermittent catheters are known to cause discomfort during insertion.1 One explanation may be that catheter eyelets deform urethral mucosal tissue.2 GentleCath™ Intermittent Catheter eyelets have a long thin shape, which is designed to reduce tissue deformation, without reducing the speed of urine flow through the catheter. Tissue Deformation Narrow eyelet shape designed to reduce tissue deformation Tissue Deformation Height GentleCath Intermittent Catheter eyelets have been shown to cause significantly lower tissue deformation than the Bard Clean-Cath™, Coloplast Self-Cath™ and Cure Medical Cure Catheter™.2* ™ Bard Clean-Cath™ Cure Medical Cure Catheter™ Learn more www.gentlecath.com/gentleeyelets * As demonstrated in an in vitro study Coloplast Self-Cath™ ConvaTec GentleCath™ In vitro testing of tissue deformation by catheter eyelets – a comparative study TM INTERMITTENT URINARY CATHETER Using an in vitro animal model and a 3D scanner, surface urethral mucosa tissue has been mapped and analysed to observe the maximum height of tissue deformation into the eyelet for different manufactured catheters. Test Method In Vitro Animal Model Each test was carried out by conducting the following steps: 1. T he catheter eyelet was pressed onto a section of porcine urethral tissue. 2. A force representative of internal urethral sphincter pressure was applied.*3,4 3. A 3D scan of the tissue surface was taken.** Measurement Internal Catheter View Measurement of the deformation of the tissue into the eyelet was calculated from the 3D scan by using the maximum distance of the urethral tissue from where the outer surface of the catheter would have been if there was no eyelet. Catheter Maximum tissue height Catheter thickness Urethral tissue Evaluated Catheters Eyelet Tissue Deformation Height 4 catheter brands of size 18Fr male were evaluated. 1.5 1.4 Results Randomization: A batch of 16 tests were conducted which consisted of testing the four catheter brands by two operators performing two repetitions. All tests were randomized with a limit that all four tests on any one urethra have to be consecutive to minimize possible drying out of the urethra when exposed to air. 1.3 Height (mm) The 95% confidence interval of maximum tissue height for the GentleCath™ product does not overlap the confidence levels for the other brands tested. This provides a 95% confidence that there is a statistically significant difference between the maximum heights of tissue deformation in the eyelets tested. (P < 0.05)1 1.2 1.1 1.0 0.9 0.8 1.27 1.33 0.7 0.6 Cure Medical Cure Catheter™ * 60cm H2O ** Calibrated scanner has a resolution of 6µm References: 1. Dellimore KH, Helyer AR, Franklin SE (2013). A scoping review of important urinary catheter induced complications. Journal of materials science. Materials in Medicine, 24(8):1825–1835. 2. Walker M, Lambrethsen J, Winther T (2014). In vitro testing of Tissue Deformation by Catheter Eyelets. Data on file. 3. Weber AM (2001) Leak point pressure measurement and stress urinary incontinence. Current womens’ health reports, 1(1): 45–52. 4. Marti F, Leippold T, John H, Blunschi N, Müller B (2006) Optimization of the artificial urinary sphincter: modelling and experimental validation. Physics in Medicine and Biology 51: 1361-1375 GentleCath is a trademark of Unomedical a/s. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. ©2014 ConvaTec Inc. AP-014757-MM Bard Clean-Cath™ 1.14 Coloplast Self-Cath™ .78 GentleCath™