H2020 Brokerage Event_Technology_13_DJS_Leicester_Jenkin
Transcription
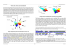
*SC5-11-2014/2015: New solutions for sustainable production of raw materials e [2015] New metallurgical systems* Novel Environmentally-friendly Ore Processing Techniques for the 21st Century Gawen RT Jenkin & Daniel J Smitha Andrew Abbottb aDepartment of Geology, University of Leicester, UK, grtj1@le.ac.uk bDepartment of Chemistry, University of Leicester, UK Conventional ore processing Ore + Energy (€) Metal + CO2 (☹) + Wastes (€ ☹, CO2 ☹) Can we do better? – Need a low energy (€) process, more environmentally compatible A new chemistry - ionic liquids • Anhydrous salts that are liquid at low temperature – Powerful solvents • • • • High selectivity in dissolution and recovery Amenable to electrochemistry Successfully used to recover metals from scrap and oxides No large volume/low concentration aqueous waste CuCl2 dissolved in different ILs BUT, must be: • Low cost • Environmentally compatible • No registration requirements - We use non-toxic biodegradable Deep Eutectic Solvents Gold dissolution by oxidation with I2 Reflected light galena BEFORE AFTER pyrite el 7 µm quartz 7 µm el = electrum (Ag:Au ~50:50 wt%) Sample: gold ore, Cononish deposit, Scotland Solution: I2 in ionic liquid, 10 mins, ~50°C Abbott et al. 2014, Electrocatalytic Recovery of Elements from Complex Mixtures using Deep Eutectic Solvents, Green Chemistry, doi 10.1039/C4GC02246G Gold dissolution and recovery Gold panned concentrate Electrodeposition from solution ~20 hours Dissolution by oxidation in ionic liquid with I2, 48 hours Abbott et al. 2014, Electrocatalytic Recovery of Elements from Complex Mixtures using Deep Eutectic Solvents, Green Chemistry, doi 10.1039/C4GC02246G Dissolution by electrolytic reduction • Change in solution colour indicates dissolution of other minerals: Ionic liquid Pyrite in ionic liquid Arsenopyrite… Pyrrhotite… Chalcopyrite… Covellite… Loellingite… Bornite… Chalcocite… Summary • We have not yet found a native metal/metalloid, sulfide, sulfosalt or telluride (e.g. calaverite AuTe2) that we cannot dissolve in DES ionic liquid. • Electrolytic recovery of Au from solution is proven (+22 other metals) – could quantitatively separate metals by different voltages. • Ionometallurgy could thus offer a whole new set of environmentally benign tools for metallurgists. • Looking for partners: – High grade complex deposits and concentrates optimum – Lower grade deposits, heap leach on the horizon Cononish electrum inclusions in pyrite (Hill et al. 2013) • Contact us: grtj1@le.ac.uk, see Gawen Jenkin, Dan Smith
Similar documents
Global De-aromatic Solvents Market, 2016 - 2022
 De-aromatic solvents, also called dearomatized hydrocarbon solvents or ultra-low aromatic solvents, are a class of hydrocarbon solvents that are characterized by the presence of paraffinic, iso-paraffinic, and naphthenic components with very low aromatic content (<2%). De-aromatic solvents are of three types, namely low flash point, medium flash point, and high flash point. These dearomatized hydrocarbon solvents find application in various industries and are used as solvents for printing inks, paints & coatings, metal working fluids, industrial and institutional cleaning, adhesives and sealants, drilling fluids, and in consumer products. They are effective alternatives to conventional solvents such as mineral spirits and mineral turpentine.
Global sales revenue of the global de-aromatic solvents market is expected to increase at a CAGR of 5.9% over the forecast period, to reach US$ 2,198.5 Mn by 2022.
De-aromatic solvents, also called dearomatized hydrocarbon solvents or ultra-low aromatic solvents, are a class of hydrocarbon solvents that are characterized by the presence of paraffinic, iso-paraffinic, and naphthenic components with very low aromatic content (<2%). De-aromatic solvents are of three types, namely low flash point, medium flash point, and high flash point. These dearomatized hydrocarbon solvents find application in various industries and are used as solvents for printing inks, paints & coatings, metal working fluids, industrial and institutional cleaning, adhesives and sealants, drilling fluids, and in consumer products. They are effective alternatives to conventional solvents such as mineral spirits and mineral turpentine.
Global sales revenue of the global de-aromatic solvents market is expected to increase at a CAGR of 5.9% over the forecast period, to reach US$ 2,198.5 Mn by 2022.