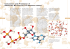GEMM THERAPY FOR CANCER
Transcription
GEMM THERAPY FOR CANCER
GEMM THERAPY FOR CANCER This document provides a comprehensive overview of GEMM Technology developed by Dr Seckiner Gorgun for Cancer Treatment. The overview is made up of the following sections: The Scientific Rationale Cellular Communication is Electromagnetic in Nature Mitochondria Plays the Key Role in Cancer and in Regulating Mitosis Irreversibly Damaged Glycoproteins in Mitochondrial Membrane Initiates Cancer Hypothesized Mechanism on Cancer and Mitosis Control The GEMM Device Cell Studies Cell Study at Ankara University Medical Faculty in 1974 Cell Study at Thailand National Cancer Institute in 1979 Cell Study at University of Bordeaux in 1983 Cell Study at the Hannover Medical School in 1989 Cell Study at the USSL Ivrea in 1993 Human Studies and Select Case Reports Case Report from Pakistan in 1977 Preliminary Clinical Study Case Reports in Turkey 1979‐1980 Case Reports from Italy between 1986‐1999 Case Reports from Turkey between 1999‐2004 Attempted Clinical Trials Clinical Trial controversy with the USSL Ivrea in Piemonte, Italy 1995 Clinical Trial Request from AOVV from Lombardia, Italy in 2004 Related Documents Torino Court Order & Expert Report of Prof Mario Maritano, Italy 1986 International Patent Device & Functions for the Modulation of Biological Processes 1997 CE Certificate & Conformity Letter, Italy 1997 State of Piemonte Sanitary Clearance Certificate, Italy 1997 Published Articles Article published at the Journal of Frontier Perspectives in 1998 Selected References Reference Letter from Dr. A.H. Nagi, Pakistan 1979 Reference Letter from Dr Haluk Nurbaki, Turkey 1980 Reference Letter from Dr Pierpaola Papurello, Italy 1997 Reference Letter from Dr Valeria Biino, Italy 1997 Reference Letter from Prof Emilio Del Giudice, Italy 2001 Reference Letter from Prof Raffaele Giovanell, Italy2001 Reference by Dr Mark Neveu, USA 2003 Guarantee Letter by Galileo Avionica, Italy 2004 Invitation by Prof Jiri Pokorny, Czech Republic 2005 Invitation by Prof Gianpiero Gervino, Italy 2006 THE SCIENTIFIC RATIONALE GEMM Technology is based on a hypothesis developed by Dr Seckiner Gorgun in the 1970s. The hypothesis has basically three major propositions: Proposition 1 The cellular communication between the atoms, molecules, structures, organelles, cells, tissues, organs of the body is primarily electromagnetic in nature and carried by radio waves. Proposition 2 Mitochondria, the energy producing organelle in the cell plays a key regulating role in mitosis (cell division) and all cancers take place when there is a specific type of damage to the mitochondria. Proposition 3 An irreversible damage to normal glycosylation (the process or result of addition of saccharides to proteins and lipids) is a universal feature and initiator of cancer. PROPOSITION 1 CELLULAR COMMUNICATION IS ELECTROMAGNETIC IN NATURE It is estimated that the average human adult body contains about 70 trillion cells. Each human cell is also estimated to contain 100 Trillion atoms. A human cell contains several different compartments and a very complex structure such as the following illustration: Generally the cellular processes within the cell are regulated by proteins that are involved in the cellular transactions. A protein is made up of smaller amino acid molecules. Their 3‐dimensional folding is closely correlated to their functioning. A typical human cell contains an average of 8 Billion proteins made up of 10‐20,000 different types. Below you can find 2 different models of protein structures showing the complex 3‐D folding.. According to the established medical explanation all communication in the body is by biochemical means. Generally two complementary shaped proteins interact with each other per the key‐lock or its modified induced fit model as per the following picture. However there is a major problem with this model. The cell is an extremely crowded environment with 100 Trillion atoms and many different molecules and structures. So how is it possible for a protein to recognize and interact its target protein among 10,000 different types of proteins as there are 100 trillion atoms and 8 billion proteins inside this densely packed human cell. The classical explanation is the random collision model. This model states that all molecules in the cell continuously collides with each other and when the complementary shaped molecules make this collision they initiate a transaction per the key‐lock or induced fit model described above. However Dr Gorgun along with several other scientists, does not agree with these commonly believed classical explanations. According to him both the key‐lock model and the random collisions hypothesis are seriously flawed and far from explaining the very delicate and smooth mechanism regulation cellular and bodily processes. Dr Gorgun hypothesized that the actual key‐lock mechanism in the cellular processes are different, and depend on the specifically coded information on the electrostatic field around the molecules. This is comparable to the hotel key cards where the specifically coded information on the static magnetic field of the key card is used as a more sensitive and selective way compared to old type of key where the sensitivity and selectivity depends on the shape of the key. In the below pictures you can see an old type of key where the shape is determinant, a new type of hotel key card where the coded information on the magnetic stripe is determinant and finally a demonstration of the electrostatic field around a molecule where the cells are using to code the necessary information to regulate transactions. Dr Gorgun also hypothesized that molecules such as proteins do not depend on random collisions to find each other. Instead they communicate via radio waves at specific resonant frequencies. All molecules are made up of atoms. Depending on the characteristics of the individual atoms and shape of the molecule they can act as a receiving and transmitting antenna. The structure and length of the molecules such as in the below right picture determines the specific resonant frequency it acts as an antenna. There are several scientists who studied the effect of radio waves at specific frequencies on different molecules on the cells. One of the leading researchers in this field is Prof Irena Cosic who developed the Resonant Recognition Model ‐RRM‐ published a series of scientific articles pointing to the role of electromagnetic waves in cellular communication. In her article namely “The effect of electromagnetic radiation (550 – 850 nm) on l‐Lactate dehydrogenase kinetics” she had noted: It has been shown in our previous research that all protein sequences with the common biological function have common frequency component in the distribution of free energy of electrons along the protein backbone. This characteristic frequency is related to the protein biological function as it was found in our previous investigations.). Furthermore, it was also shown that proteins and their targets have the same characteristic frequency in common. Thus, it can be postulated that RRM frequencies characterize not only a general function but also a recognition/interaction between the particular protein and its target at the distance. Thus, protein interactions can be considered as the resonant energy transfer between the interacting molecules. This energy can be transferred through oscillations of a physical field, possibly electromagnetic in nature. Results reveal the LDH activity was modulated by the EMF exposures at the computationally predicted frequencies. The RRM concept presented provides new insights into proteins susceptibility to perturbation by electromagnetic radiation and possibility to program, predict, design and modify proteins and their bioactivity. Below you can see a list of selected RRM frequencies for different functional group of proteins and DNA Regulatory sequences. This is a very clear indication that proteins in the human body can communicate and interact at the specific resonant frequencies. For additional information in this topic you can visit Prof Mae Wan Ho ’s article The Real Bioinformatics Revolution : Proteins and Nucleic Acids Singing to One Another? appeared in the Institute for Science in Society Portal. Another significant study which provides additional evidence that cells can communicate by means of radio waves was published by the Italian Nuclear Physicist Prof Emilio Del Giudice et al in 1989 with the title “Magnetic Flux Quantization and Josephson Behaviour in Living Systems”. The below pictures taken from the study clearly demonstrates the effect that during the mitosis the yeast cell Saccaromyces Cerevisiae was emitting a radio frequency signal centering around 7.0 MHz as recorded by the spectrum analyzer. 7.0 MHz Radio Frequency emission recorded during cell mitosis of Saccaromyces Cerevisiae There are numerous other studies demonstrating the interaction between electromagnetic waves and living matter. Over 10,000 such studies are accessible at the EMF Portal. As a summary Dr Gorgun states that all living systems heavily depend on radio waves to regulate biological transactions. For transmitting several commands to numerous parts of the system at the same time the central command system (such as brain) transmits radio signals that are received by the receiving antennas that are tuned to the very specific resonant frequency. Individual proteins also recognize their target protein counterparts at a distance and make the interactions by electromagnetic means. Very frequently also several other atoms and molecules such as Ca ions, hormones, enzymes, etc are used to carry messages around the body. Such messages are coded on the surrounding electrostatic field of the messenger molecules and decoded when they interact with their targets to initiate the relevant transaction. According to Dr Gorgun the reason why such an enormous flow of radio waves cannot be sensed by current sensing systems is due to the fact that instead of high energy containing electric photons, the radio waves used in molecular communication is primarily managed by tens of millions of times less energy containing magnetic photons. The concept of magnetic monopoles (an isolated north or south magnetic pole) was first hypothesized by one of the founders of Quantum Physics Theory, the Nobel Laureate Paul Dirac and magnetic photons also were first hypothesized by another Nobel Laureate in Physics Dr Abdus Salam. Despite the common agreement among theoretical physicists that magnetic monopoles/photons, yet no scientists were experimentally able to demonstrate their existence. In the 1970s Dr Gorgun developed a technique to isolate the magnetic photons from an electromagnetic wave and amplify them through resonance which he named the “Gorgun Principle” By the means of magnetic photons that are used in nature to carry information he developed a way to interact with molecules in their native resonant frequency language. PROPOSITION 2 MITOCHONDRIA PLAYS THE KEY ROLE IN CANCER AND IN REGULATING MITOSIS The mitochondria is the organelle responsible for most of the energy production of the cells in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The cells use glucose as a fuel to obtain energy. The cells can convert glucose to ATP either in the cytoplasm with a process called glycolysis generating 2 ATP molecules, or they can utilize the mitochondria with a mechanism called Krebs Cycle where 2 + 34 ATP molecules are produced. Below you can see the illustration of the mitochondria and the different ATP producing pathways. For more than 70 years most cancer researchers heavily depend on the Warburg’s Hypothesis which was postulated by the Nobel laureate Otto Heinrich Warburg in 1924. He hypothesized that cancer, malignant growth, and tumor growth are caused by the fact that tumor cells mainly generate ATP by non‐oxidative breakdown of glucose or glycolysis. This is in contrast to "healthy" cells which mainly generate energy from oxidative breakdown of pyruvate. Pyruvate is an end‐product of glycolysis, and is oxidized within the mitochondria. Hence and according to Warburg, cancer should be interpreted as a mitochondrial dysfunction. Warburg reported a fundamental difference between normal and cancerous cells to be the ratio of glycolysis to respiration; this observation is also known as the Warburg effect. Many researchers took this information as granted and believed that the mitochondria has a limited effect in mitosis and become dysfunctional in cancer. In 1970s Dr Gorgun hypothesized that it is the Mitochondria plays a key role in mitosis and certain damages to the mitochondria which causes it to malfunction (to overproduce ATP) will trigger the premature, uncontrolled cell division which is called cancer. This is an apparent contradiction to the Warburg’s hypothesis. However several new studies provided clear evidence that, the long held belief of the Warburg effect could be wrong. In the next page you can find some published studies regarding the role of glycolysis and mitochondria in cancer. Cancer metabolism: facts, fantasy, and fiction Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2004, vol. 313, no3, pp. 459‐465 Zu X, Guppy M The concept of a glycolytic cancer cell was introduced by Warburg over 70 years ago. This perception has since become the rationale that drives a considerable proportion of basic research on cancer, and it influences the current strategies for the diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of cancer. Here we review the data from the last 40 years on this issue. We conclude that there is no evidence that cancer cells are inherently glycolytic, but that some tumours might indeed be glycolytic in vivo as a result of their hypoxic environment. Contribution by different fuels and metabolic pathways to the total ATP turnover of proliferating MCF‐ 7 breast cancer cells The Biochemical Journal 2002 May 15;364(Pt 1):309‐15 Guppy M, Leedman P, Zu X, For the past 70 years the dominant perception of cancer metabolism has been that it is fuelled mainly by glucose (via aerobic glycolysis) and glutamine. Consequently, investigations into the diagnosis, treatment and the basic metabolism of cancer cells have been directed by this perception. However, the data on cancer metabolism are equivocal, and in this study we have sought to clarify the issue. Using an innovative system we have measured the total ATP turnover of the MCF‐7 breast cancer cell line, the contributions to this turnover by oxidative and glycolytic ATP production and the contributions to the oxidative component by glucose, lactate, glutamine, palmitate and oleate. The total ATP turnover over approx. 5 days was 26.8 lmol of ATP[10( cells−" [ h−". ATP production was 80% oxidative and 20% glycolytic. Contributions to the oxidative component were approx. 10% glucose, 14% glutamine, 7% palmitate, 4% oleate and 65% from unidentified sources. The contribution by glucose (glycolysis and oxidation) to total ATP turnover was 28.8%, glutamine contributed 10.7% and glucose and glutamine combined contributed 40%. Glucose and glutamine are significant fuels, but they account for less than half of the total ATP turnover. The contribution of aerobic glycolysis is not different from that in a variety of other non‐transformed cell types. Cancer's sweet tooth Cancer Cell , Volume 9 , Issue 6 , Pages 419 – 420 T . Bui , C . Thompson Even in the presence of an adequate oxygen supply, many tumors metabolize the majority of the glucose they take up through glycolysis. It has been a long‐held belief that this glycolytic phenotype is due to cancer‐specific defects in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. In this issue of Cancer Cell, Fantin et al. now report that most tumor cells have a substantial reserve capacity to produce ATP by oxidative phosphorylation when glycolysis is suppressed. These new data add to mounting evidence that the high rate of glycolysis exhibited by most tumors is required to support cell growth rather than to compensate for defect(s) in mitochondrial function. Mitocans: mitochondrial targeted anti‐cancer drugs as improved therapies and related patent documents Recent Patents Anticancer Drug Discov. 2006 Nov ;1 (3):327‐46 Ralph SJ, Low P, Dong L Mitochondria are proving to be worthy targets for activating specific killing of cancer cells in tumors and a diverse range of mitochondrial targeted drugs are currently in clinical trial to determine their effectiveness as anti‐cancer therapies. The mechanism of action of mitochondrial targeted anti‐cancer drugs relies on their ability to disrupt the energy producing systems of cancer cell mitochondria, leading to increased reactive oxygen species and activation of the mitochondrial dependent cell death signaling pathways inside cancer cells. We propose that this emerging class of drugs be called "mitocans", a term that reflects their mitochondrial targeting and anti‐cancer roles. However, it is clear from the present studies that mitocans offer great potential as effective and exciting new developments in cancer therapy, providing direct activation of cancer cell death by mitochondrial mediated apoptosis and that this complements the other pathways by which existing treatments kill cancer cells. Undoubtedly, mitocans will become an integral part of modern weaponry in the fight to eliminate cancer. A very recent study dated 25 April 2008 provided new insights into the mitochondria’s role in cell division. The following article can be accessed at this link Yeast shows what drives cells to divide Mitochondria have been found to also be the driver with regard to cell division, according to a group of biochemists who say this discovery could play a large role in finding cures for many human diseases. The scientists studied yeast cells and found that mitochondria, which generate 90 percent of the cell’s energy, can be the deciding factor behind how fast cells divide. The finding by Michael Polymenis and Mary Bryk and their research groups is published today in the open‐access journal PLoS Genetics. The finding changes the traditional view of the mitochondrion from an “energy depot” at the service of its larger cellular host to a “command center” that directs cell division. The researchers used regular baker’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) ‐ commonly used in bread, wine and beer making ‐ because many of the yeast cell’s processes are similar to those in human cells. From unicellular yeast to complex mammals, the process is the same. The job of a cell is to divide and grow. Metabolism takes in “food” and turns it into fuel and building blocks for DNA replication and gene expression. But when these processes falter, diseases can result. Too much cell division too quickly, for example, is typical of cancerous cells. Conversely, poor metabolism ‐ stemming from mitochondrial deficiencies ‐ is at the root of damage to various organs such as the brain, heart, skeletal muscles, and liver. All of the body processes that require a lot of energy are impacted by this, and at least 1 in every 4,000 people worldwide suffer from mitochondrial deficiencies that result in problems with normal development, motor control, vision, hearing, or liver and kidney function. Alternatively, there are times when speeding cell division might be useful as with wound healing and plant or crop production. If we can understand the basic pathway that regulates cell division, we can think of ways to tweak the different steps in that path with therapeutics to help people who have problems with these high‐energy organs. The research showed that when a yeast cell’s mitochondria decided to “turn on the switch,” the cell’s nucleus, which carries most of the genetic material, received the message and cell division began. So now we need to connect that link. We need to understand how and when the mitochondria send the message. If we know how the message is sent, we might be able to control it. An Increase in Mitochondrial DNA Promotes Nuclear DNA Replication in Yeast. 2008 PLoS Genetics 4(4) Blank HM, Li C, Mueller JE, Bogomolnaya LM, Bryk M, Polymenis M Coordination between cellular metabolism and DNA replication determines when cells initiate division. It has been assumed that metabolism only plays a permissive role in cell division. While blocking metabolism arrests cell division, it is not known whether an up‐regulation of metabolic reactions accelerates cell cycle transitions. Here, we show that increasing the amount of mitochondrial DNA accelerates overall cell proliferation and promotes nuclear DNA replication, in a nutrientdependent manner. The Sir2p NAD+‐dependent de‐acetylase antagonizes this mitochondrial role. We found that cells with increased mitochondrial DNA have reduced Sir2p levels bound at origins of DNA replication in the nucleus, accompanied with increased levels of K9, K14‐acetylated histone H3 at those origins. Our results demonstrate an active role of mitochondrial processes in the control of cell division. They also suggest that cellular metabolism may impact on chromatin modifications to regulate the activity of origins of DNA replication. PROPOSITION 3 IRREVERSIBLY DAMAGED GLYCOPROTEINS IN MITOCHONDRIAL MEMBRANE INITIATES CANCER Glycosylation is the process or result of addition of saccharides to proteins and lipids. The end products are Glycoproteins, that are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to their polypeptide side‐chains. Glycoproteins are often attached to membranes, where they play an important role in cell‐cell and nucleus‐organelle interaction, communication and recognition. Below is an illustration of glycoproteins in the cell membrane with antenna like glycan chains. Membrane Glycoproteins respond to the messages they obtain from environment and they initiate special functions based on the external stimuli they received. A universal feature of all cancer cells is that they have damage to the delicate structure of their glycoproteins. There are several published studies in this field. Glycosylation defining cancer malignancy: New wine in an old bottle Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences PNAS | August 6, 2002 | vol. 99 | no. 16 | 10231‐10233 Hakomori S Aberrant glycosylation occurs in essentially all types of experimental and human cancers, as has been observed for over 35 years, and many glycosyl epitopes constitute tumor‐associated antigens. A long‐standing debate is whether aberrant glycosylation is a result or a cause of cancer. Many recent studies indicate that some, if not all, aberrant glycosylation is a result of initial oncogenic transformation, as well as a key event in induction of invasion and metastasis. Glycosylation promoting or inhibiting tumor cell invasion and metastasis is of crucial importance in current cancer research. Nevertheless, this area of study has received little attention from most cell biologists involved in cancer research, mainly because structural and functional concepts of glycosylation in cancer are more difficult to understand than the functional role of certain proteins and their genes in defining cancer cell phenotypes. Glycosylation appears to be considered ‘‘in the shade’’ of more popular topics such as oncogenes and antioncogenes, apoptosis, angiogenesis, growth factor receptors, integrin and caderin function, etc., despite the fact that aberrant glycosylation profoundly affects all of these processes. Dr Gorgun hypothesized that the glycan chains of the glycoproteins that are commonly named as antenna indeed acts like an antenna and they respond to radio waves at the selective resonant frequencies determined by their structure and length. The following study also provides evidence that glycoproteins can detect and respond to electric fields and that their mass is a critical parameter. Glycoproteins bound to ion channels mediate detection of electric fields: a proposed mechanism and supporting evidence Bioelectromagnetics. 2007 Jul;28(5):379‐85 Kolomytkin OV, Dunn S, Hart FX, Frilot C , Marino AA. The mechanism by which animals detect weak electric and magnetic fields has not yet been elucidated. We propose that transduction of an electric field (E) occurs at the apical membrane of a specialized cell as a consequence of an interaction between the field and glycoproteins bound to the gates of ion channels. According to the model, a glycoprotein mass (M) could control the gates of ion channels, where M > 1.4 x 10(‐18)/E, resulting in a signal of sufficient strength to overcome thermal noise. Using the electroreceptor organ of Kryptopterus as a mathematical and experimental model, we showed that at the frequency of maximum sensitivity (10 Hz), fields as low as 2 microV/m could be detected, and that the observation could be explained if a glycoprotein mass of 0.7 x 10(‐12) kg (a sphere 11 microm in diameter) were bound to channel gates. Antibodies against apical membrane structures in Kryptopterus blocked field transduction, which was consistent with the proposal that it occurred at the membrane surface. Although the target of the field was hypothesized to be an ion channel, the proposed mechanism can easily be extended to include other kinds of membrane proteins. HYPOTHESIZED MECHANISM ON CANCER AND MITOSIS CONTROL There are several factors such as genetic disorders, free radical damage, ionizing radiation etc. that may damage the delicate glycan structure of the glycoprotein sensors at the membranes of mitochondria. The chromosomes, following the messages received as a result of the variations of potential in the cytoplasmic membrane, activate through electromechanical effects the emission of radio messages by the genes that regulate cell dynamics for normal cell functions or for the mitochondrial activities for ATP production. Under normal circumstances these sensors respond to radio messages from the genes in the nucleus at a specific frequency to regulate ATP production in the mitochondria. When the glycan chains of the glycoprotein sensors are irreversibly damaged (chains are broken and reduced in size) their impedance are lowered, antenna characteristics are changed thus they can no longer discriminate between the signals they obtain from the environment and almost continuously trigger ATP production in the mitochondria. The cancer cell would therefore go into a premature, forced mitosis due to the excess production of ATP. This forced, premature mitosis will trigger further damage to the structures and control mechanisms in the cell. To correct this problem static magnetic fields and square wave pulsed electric fields from the GEMM device are used to act on the mitochondrial membrane, which will put the damaged glycoprotein sensors in a repair mode and increase their impedance through the lengthening of their glycan chains. A pulsed electromagnetic field in phase with the electrical signal is used to interfere with the communications between the genes and the protoplasmic glycoprotein complexes involved in the promotion of cell mitosis. It is thought that the impedance of the mitochondrial membrane sensors to the messages coming from the genes increases with the electromagnetic GEMM treatment but this effect is different depending on the initial glycoprotein structures and the impedance increases much higher for more malignant tumor cells (the highest impedance for undifferentiated tumor cells). This is related to a greater alteration of the sensors of the undifferentiated tumors and therefore to their greater predisposition to the bond with glycan chains. The undifferentiated cancer cells, because of the high impedance induced on the mitochondrial membrane by the electromagnetic treatment, stop producing ATP and therefore enter into apoptosis initiated necrosis. The effect of the GEMM treatment on the differentiated tumor cells are different and the glycoprotein sensors of such cells will have an impedance level which is still sensitive to some messages coming from the chromosomes promoting the normal production of ATP, so although these cells will not enter into mitosis; they continue to live in a quiescent state (vegetative form of life). The normal cells are not influenced by the electromagnetic treatment as the impedance of their mitochondrial sensors is not modified and remain sensitive to messages that arrive from the chromosomes for the activation of the ATP synthesis. THE GEMM DEVICE GEMM generates Magnetic Photon Waves at the desired frequency, modulation and amplitude as required for the treatment. The radio waves used in the treatment are in the AM frequency (kilohertz) range. The typical output power of the antenna is 0.25 Watts. The system is programmed individually depending on the patient’s various parameters. Patients need to lay down the treatment beds during treatment sessions that generally lasts around 30 minute. There are typically 5 sessions per week and the treatment duration may last between 1‐4 months depending on the condition of the patient and the size, location and histopathology of the tumor. The GEMM GeneratorModule Treatment Beds The application is very safe. No thermal or ionizing radiation is involved. As seen in the following picture a Gamma Ray or X‐Ray used in standard Radiotherapy applications utilizes very high frequency electromagnetic waves that contains photons having energy levels of approximately 100,000 Electron Volts. GEMM Device operates at the AM frequency (kilohertz) range and a corresponding electric photon has an average of 0,00000001 electron volts. As noted earlier GEMM device utilizes the so‐ called magnetic photons with millions of times of less energy per photon corresponding to the electric photon at the same frequency. Therefore almost no energy is applied to the tumor but the radio waves are only used to regulate the processes by triggering interactions at the specific resonant frequencies. Additionally during the treatment a separate radio signal is transmitted from the GEMM device that will block the glycolysis mechanism, a preferred method utilized for the cancer cells to compensate for the energy requirements when needed. The combined approach will practically block all available energy sources for the cancer cell. CELL STUDIES AT ANKARA UNIVERSITY IN 1974 To test his hypothesis Dr Gorgun did several cell studies in different institutions in Turkey, Germany, France, Italy and Thailand. The following pictures of neoplastic HeLa cells in contrast phase seen through the microscope are taken during the experiments held at the University of Ankara in 1974. The culture was exposed to GEMM radio waves for a period of about three hours. As a consequence of the GEMM treatment the cancer cell that can no longer produce ATP both from the glycolysis reaction and through the oxidative phosphorylation on the mitochondria. The energy starving cancer cells migrate to each other, try to initiate a fusion to unite their cytoplasm with sister cells to share their ATP in order to survive. A maximum of 4 sister cells can unite their cytoplasm in this fusion process and then necrosis occurs . Progressive fusion and necrosis of the HeLa cancer cells following the GEMM Treatment CELL STUDIES AT THAILAND NATICONAL CANCER INSTITUTE 1979 In 1979 Dr Gorgun engaged in cell studies at the Thailand National Cancer Institute in Bangkok. Hehas worked on lymphoblastoid cell lines P3H3 and P3HR1. The report issued by Dr Petcharin Srivatanakul, confirms the efficacy of GEMM treatment on the cancer cells. Above you can see the first page of the report and in the next page the last page of the report. The outcomes of the study has been presented by Dr Seckiner Gorgun at the 6th Balkan Medical Congress held in Ankara, Turkey between 9‐13 September 1979 with the title named: “Sur le traitement du cancer per la controle de la mitose” “Treatment of cancer by the control of mitosis” The corresponding documents can be viewed in the next page. CELL STUDIES TA THE UNIVERSITY OF BORDEAUX 1983 In 1983 Dr Gorgun has worked with the renowned immunologist Prof Raymond Pautrizel at the University of Bordeaux and demonstrated the efficacy of GEMM on Trypanosoma and Plasmodium. Dr Gorgun with Prof Raymond Pautrizel Dr Gorgun at his laboratory in university of Bordeaux CELL STUDIES AT HANNOVER MEDICAL SCHOOL IN 1989 Dr Gorgun later demonstrated the effect of GEMM Therapy on cancer cells to Prof Hans‐Joachim Schmoll who has been the chief of the Oncology and Hematology Clinic at the Hannover Medical University. Prof Hans‐Joachim Schmoll is currently the Director of Department of Hematology & Oncology at the Martin‐Luther University in Germany. He is a renowned name in Oncology with 18 published books and over 400 journal articles. He is the associate editor of Cancer Research, Editor in Chief of Onkologie, Scientific Advisory Board Member of European Journal of Cancer and also the Annals of Oncology. Currently he is the Chairman of the German Association of Medical Oncology. Below you can find the microscope pictures taken at Dr Schmoll’s laboratory in Hannover Medical University during the in vitro experiments made with GEMM on the cancer cells of the CCL‐178 line, the adenocarcinoma of the colon. GEMM Treatment for 2 hours initiated the progressive fusion and necrosis where the accommodation of the cytoplasms of necrotic cancer cells in big lumps can be easily observed. Additional cell lines used during the experiment were testicular carcinoma cell line H 32, H 12.1 H 1411 and stomach carcinoma M 51. Fusion, necrosis and evident accommodation of necrotic tissues following GEMM Treatment The following is the reference letter issued by Prof Hans‐Joachim Schmoll to Dr Gorgun which confirms the efficacy of GEMM treatment on cancer cells. CELL STUDIES AT THE LABOROTORIA DI FISICA SANITARIA IVREA, ITALY 1995 During the research at the Laborotoria di Fisica Sanitaria Ivrea, the cancer cells treated with GEMM were examined with an electron microscope and they show ultrastructural alterations in the following areas: • Cytoskeleton fiber ‐ at the structure alteration level with an increase in fibers compared to the control and with a more irregular disposition and orientation • Mitochondrion ‐ a different orientation of the mitochondrion crests and an alteration of the mitochondrion matrix which appears dishomogeneous and pycnotic compared to the control • Autophages ‐ intra‐cytoplasmic bodies in many cells Moreover, the following can be noted: • Chromatin degeneration • Thickening of the chromatin at the nuclear membrane level • Nucleus vacuolisation • Mitochondrial degeneration These types of alterations, especially at the nuclear level, suggest the hypothesis that an apoptotic type of phenomenon was induced by the treatment. Electron Microscope Pictures Dr Gorgun also conducted several mice studies the first being held Marburg Universitat Klinik und Poliklinik fur‐Nuclearmedizin, Radiologiezentrum der Philippsuniversitat Marburg/Lahn at the Institute for Biophysics and Nuclear Medicine with Prof Schaumloeffel in 1974. Before being subjected to GEMM treatment, the mice were inoculated with three different types of histopathological material namely Yoshida Solid, Asditis and Walker. GEMM application eliminated the progression of the cancer. HUMAN STUDIES AND CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT IN PAKISTAN 1977 Dr Gorgun began to treat patients with GEMM Therapy technique back in 1977 while he was still a student at the Medical School in Pakistan (by law he was allowed to do so). Due to the fact that the treatment is very effective and providing quick returns for aggressive tumors made up of indifferentiated cells, he obtained some amazing outcomes even right after the very first application. The following letter is send to the Morning News Newspaper published in Karachi, Pakistan by S.M. Afzal in response to the Pakistan Medical Association calling Dr Gorgun a “phoney” and that people should not take a ride on him. Below you can see the patient’s face before and 3 hours after the very first GEMM treatment. As clearly noticed, she had significant swelling in the first picture and looked almost unconscious. The swelling subsided completely & she was quite conscious in the second picture with no signs of pain. PRELIMINARY CLINICAL STUDY AT ANKARA NUMUNE HOSPITAL 1979‐1980 After completing his medical education in Pakistan and his studies at the Thailand National Cancer Institute, Dr Gorgun came back to Turkey and per the permission of the ethical committee of Ankara Numune Hospital (one of Turkey’s largest state hospitals) he began to treat terminal cancer patients that did not respond to conventional treatments. The following is from the Reference Letter issued by the Hospital’s Chief Physician Dr Turhan Temucin (90‐312‐ 426 1602) on behalf of the ethical committee granted the permit: The following pictures belong to hemangiosarcoma patient Ilhan K. whom Dr Gorgun treated at the Numune Hospital. The following is from the voice recordings from a Seminar held at the Ankara University by the Head Physician of the Ankara Numune Hospital Dr Turhan Temuçin and the Head Physician of the Ankara Oncology Hospital Dr. Haluk Nurbaki where they were advising the effects of GEMM Therapy on patients: “The hemangisarcoma patient was considered a terminal case by the clinic headed by Dr Mustafa Sinav. The tumor was inoperable and he had no option but amputation. Although it might be possible to stop bleeding with radiotherapy we were not able to stop its bleeding even with high dose and the patient was given 2 units of blood per day. While he was scheduled for amputation he was considered eligible for this new therapy. In his left leg he had a tumor in the size of the head of a child that was continuously bleeding causing anemia and debility. With the protocol number 568/809 he was handed to the team for 8‐9 days of treatment. Following the first treatment on November 12, the bleeding of the patient completely seized. Afterwards with follow up treatment the mass was downsized to an orange. And as the tumor mass became operable, it was removed by a surgical team headed by Dr Yılmaz Kadioglu.” Click to hear this from his own words http://www.youtube.com/v/3TCNx6aaZpo Patient Mehmet B. who was suffering from malignant melanoma was also treated by GEMM Therapy. The following is the explanation of the case by Dr Turhan Temucin during the seminar. The patient Mehmet B. was from Manisa. His leg toe was amputated in Istanbul. 1 year later due to lymph flow he had several metastases from the leg to the haired skin of the head due to malignant melanoma. Especially due to the adenopathies, the metastatic masses in his head the patient could not sleep. He was complaining from severe pain. Following the first treatment the two metastatic nodules in his head bursted, drained away and dried. His pain disappeared, his insomnia disappeared. The first picture taken at the beginning of the treatment shows the necrotic tissues appearing in pop up packets near the lesion. The second picture is taken at a later part of the treatment where the tumor became considerably inactive and begins to dry. The pictures of the leg show different markings taken at different times of the treatment showing the initial size of the lesions and their respective shrinkage. In the last picture the lesion had a more dull appearance as it became very inactive. CASE REPORTS FROM ITALY 1986 ‐ 1999 As of 1986 Dr Gorgun initiated GEMM Therapy at a clinic in Torino together with Prof Alberto de Renzo. The application has been halted but the GEMM device has later been released by the order of Court of Torino. After obtaining the clearance Dr Gorgun together with Prof Alberto De Renzo continued to treat patients at the Casa di Cura “Major” in Torino Italy. The following is Prof. Alberto De Renzo’s reference letter who has been the Medical Director of Casa di Cura “Major”. One of the first patients Dr Gorgun treated in Italy was Mrs. Angela V. (fgermano.fg@libero.it) who was suffering from Retroperitoneal Leimyosarcoma with very poor prognosis. Her tumor was almost 50 cm in diameter which infiltrated to vital organs and the aorta and was inoperable. She did not respond to chemotherapy and due to the pressure of tumor she had circulation problems, severe abdominal pain significant swelling in the legs due to compression of lower vena cava, hydronephrosis due to urethral compression and considered to be a terminal case given only few weeks. During the first application her abdominal circumference decreased by 12 cm pointing a significant shrinkage of the tumor. After a total of 11 applications she was absolutely fine, her tumor shrank by 90% which later completely disappeared. She has been healthily living since then. Below pictures shows the condition of the tumors before treatment and herself with Dr Gorgun after the treatment. Another very impressive case which clearly shows the immediate destructive effect of GEMM Therapy on cancer cells is Mrs. Giuseppina B. who had a mastectomy for breast cancer. However there was recurrence and widespread metastasis as seen in her X‐Rays. After the first application the necrotic tissues begin to pour away from her chest as a clear indication of the quick efficacy of the treatment. Mr. Massimo M. was diagnosed with plasmacytoma in the tibial region who had decalcification, serious bone erosion and significant pain preventing him from walking. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy had no effect. Following his GEMM Treatment the pain disappeared, the bone recalcified, pathological erosions disappeared and he was able to walk again. This is a good example of the normalizing effects of GEMM Therapy that not only eliminated the tumor but initiated the reconstruction and recalcification of the damaged bone. Patient Sebastiana C. age 25 has been diagnosed with breast cancer in May 1987. She had radical mastectomy of her left breast followed by chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Despite maximum medical intervention she had widespread metastasis all over her bones. The scintigraphy report of May 1989 when she was admitted to GEMM Therapy states she had several osteolytic lesions in the examined bone segments especially in the intersection of the collar bone with the left shoulder, disseminating all through the vertebral column, and finally causing a fracture in the ischiopubic part of the femur that prevents the patient from walking. The outcome of the GEMM Therapy was amazing. The osteolytic lesions disappeared and furthermore there was bone recalcification that allowed the fracture to be healed. Following the therapy she was able to walk again and reclaimed her health. Before the therapy she could not walk After the therapy back to normal CASE REPORTS FROM TURKEY 1999 ‐ 2005 Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is one of the most aggressive primary brain tumors, with a final mortality rate close to 100% despite maximal treatment. Advancements in the past decades have not significantly increased the overall survival of patients with this disease. The recurrence of GBM is inevitable, its management often unclear and case dependent. Patient Hatice T., female, age 22, has been diagnosed as GBM and operated at a hospital in London in 2001 and following the resurrence, his doctors has a prognosis with less than 6 months. Hatice T. was suffering from symptoms such as fatigue, uncertainty about the future, motor difficulties, drowsiness, communication difficulties, and headaches. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Uk-O5AloSFs MRI taken before GEMM Therapy The treatment of Hatice T. lasted for almost 4 months and most of her symptoms disappeared within the first few weeks of the GEMM Therapy. Patient Hatice T. appeared in several televisions and newspapers in Turkey and England. The video clips of her television appearances almost 2,5 years after GEMM Therapy in 2004 shows her perfect condition. MRI Taken right after GEMM Therapy MRI after treatment shows the shrinkage of tumors. Last MRI images show no evidence of tumor. Another recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme patient, Sema T., age 26 has also been successfully treated by GEMM Therapy in 2004 . Her surgery was followed by radiotherapy chemotherapy. Following the recurrence she had been operated for the second time but the tumor continued to progess. She also had serious symptoms when accepted for the therapy. Her treatment lasted around 3 months. Sema T. also appeared at the television to advise about her condition and the outcome of her GEMM Therapy. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PP7LHX0JX0 CLINICAL STUDY ATTEMPT AT U.S.S.L. IVREA, ITALY 1995 In 1995 Dr Gorgun agreed to participate in a clinical trial to assess the efficacy of GEMM therapy. A clinical trial with the participation of the State of Piemonte Health Directore has been approved by the ethical committee and the study is initiated at the U.S.S.L No.9 Ivrea Hospital as below: However Dr Gorgun later understood that his GEMM Device has been copied and a separate application for a parallel trial at the USSL – 9 Ivrea hospital was planned without his involvement on the duplicate GEMM Device. He immediately took legal action to terminate the clinical trials. The attemped clinical trial with a duplicate GEMM Device and Dr Gorgun’s counter legal offensive issue became a big scandal has been extensively covered in several Italian newspapers. In July 2004 a team headed by Prof Piergiorgio Spaggiari, the General Director of Azienda Ospedaliera della Valtellina e della Valciavenna visited Istanbul and officially invited Dr.Gorgun for collaborating in observational clinical studies of GEMM Therapy in Italy. Dr Gorgun declined the request due to the previous unfortunate experience he had in Italy. Details of the invitation is as follows: Per the four‐year program of collaboration between the State of Lombardia and World Health Organization on the appraisal and use of the complementary medicine in clinical practice in the State Sanitary Society between 2002 – 2004, the regional committee of Lombardia approved with no: VII/13235 dated 9 June 2003, and asked me to communicate the interest of our hospital group Azienda Ospediliera establish a clinical study to assess the scientific content with additional observational studies, by our specialists whose object will be focused on the benefit of important experiences and mature results you have obtained with your therapies. TORINO COURT ORDER, ITALY 1986 Dr Gorgun has not been warmly welcomed by the Medical Community. In 1986 after treating few patients he has been challenged by the Italian Ministry of Health and GEMM Device has been seized. However after the case has been thoroughly reviewed by the Court of Torino which considered a very positive report of its appointed expert Prof Mario Maritano stating that the therapy is not only safe by also seemingly beneficial the Court made its final ruling releasing the system and allowing the therapy. INTERNATIONAL PATENT 1997 Dr Gorgun published a patent dated 17 April 1997 with International Publication Number WO 97/13549 to secure the intellectual rights of his technology. However condition specific new patents can easily be issued to provide Intellectual Property protection. CE CERTIFICATION, ITALY 1997 On 3 August 1997 Dr Gorgun obtained a CE certificate from Comtest Italia for his Generatore Elettro Magnetico Modulato GEMM‐001Sytem with Report No 97/06/001/PC. DECLERATION OF CONFORMITY, ITALY 1997 HEALTH CLEARANCE CERTIFICATE 1997 On 22 September 1997 Dr Gorgun also obtained a Clearance Certificate from Regione Piemonte Assessanato Alla Sanita with No 71/775/50 to use his system on patients for therapeutic purposes. FRONTIER PERSPECTIVES ARTICLE 1997 In 1997 Prof Beverly Rubik, the Founding Director of the Center for Frontier Sciences at the Temple University in Florida flew to Italy to meet with Dr Gorgun and get to know about the technology. After interviewing several patients and renowned scientists such as renown Italian Physicists Prof Giuliano Preparata and Prof Emilio Del Giudice, she invited Dr Gorgun to publish an article at the peer review Journal for Frontier Scientists which contains key information regarding the mechanism of GEMM as well as several case studies. The article is published in 1998 Journal Volume 7, Number 2, Fall edition, ISSN:1062‐4767. Prof Beverly Rubik, Prof Giuliano Preparata, Prof Emilio Del Giudice, Dr Gorgun and others in front of the GEMM Device at the Treatment Center in Torino, Italy. Studies on the Interaction Between Electromagnetic Fields and Living Matter Neoplastic Cellular Culture Suleyman Seckiner Gorgun Collegno, Italy Neoplastic Cell Culture The study of the interactions between electromagnetic fields and living matter has become a fertile field for research in the last century, even though these phenomena have been empirically observed by various civilisations since ancient times (1, 2). Considerable experimental evidence today points to the possibility of modulating biological functions and structures in a controlled way by applying electromagnetic fields and, vice versa, the possibility of detecting and measuring endogenous electrical currents in living organisms and their components (3, 4). There are two types of electromagnetic effects on living matter: thermal effects and non‐thermal effects (5, 6, and 7). Thermal effects induce an increase of entropic disorder in the target, until at adequate frequencies and power levels, the effects of ionisation develop. The non‐thermal effects are not the result of the transfer of erratic movement by means of an increase of kinetic energy, but rather, in line with the theories of the coherence of condensed matter, they can transmit information that would produce order in the bio‐structures involved. The information content of the electromagnetic waves would depend strictly and specifically on the waveform, the string of waves, and the time sequence of their modulation. In fact, specific variations in the configuration and temporal exposure patterns of extremely weak electromagnetic fields can produce highly specific biological responses, similar to pharmaceutical products (8, 9). These effects are attracting considerable scientific interest mainly because an electromagnetic wave is easily modulated and thus is an excellent means for the transmission of information. (10) Studies carried out by various writers suggest the possibility of nonthermal effects; they include Gorgun (16, 17, 18), Frohlich (11, 12), and Tsong (13, 23, 24, 25, 26). Based on these studies, it is reasonable to consider patterns in living matter that take into account the electromagnetic components of biological structures. Every cell, for instance, is made up of biological and chemical components that can be described in simpler and simpler terms down to the cell’s elementary molecular constituents. But the cell itself and its internal and external interactions can also be considered in terms of electric and electromagnetic interactions and relationships (1, 3, 6, 27, 28, 29, 30, 84, and 85). Numerous experimental works have shown the possibility of modifying and controlling the selective permeability of the cell membrane by transmitting electromagnetic waves. This leads to the possibility of verifying the specific reactions of healthy cells compared to the reactions of pathological cells and subsequently to select target cells on which to act for clinical purposes. Pathological cells resonate differently from healthy cells due to a different tissue composition. On these bases, various authors have noted the modulation of some cell functions, from ionic membrane pumps to many cytoplasmic enzyme reactions, including those connected with cell replication (6, 13, 14, 16, 69, 84, 85). From these studies it has been seen that these effects can be obtained from low intensity electromagnetic waves (under 1 watt) and specific frequencies (within the range of 1 Hz to 50 MHz). Along this line, preliminary observations performed in vitro have shown alterations of the cell morphology, the halt to proliferation, fusion, and necrosis in lymphoblastoid cell lines and some neoplastic lines subjected to specifically modulated electromagnetic radiation. Reported here are some demonstrative examples to show the biological effects of electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic waves have a power of 0.25 watts and are in the kilo‐ and megahertz ranges. They do not produce thermal effects on the bio‐structures and have been modulated according to the patterns elaborated by Gorgun. The examples presented here are indicative of significant biological and clinical effects both in vitro and in vivo. The action of these electromagnetic waves on neoplastic cell culture produces fusion and takes place through alteration of the cell potential (Grade 1), whereas cell necrosis takes place with the alteration of the cell structure (Grade 2). Fig 1 Fig 3 Fig5 Fig 2 Fig 4 Cell Fusion (Grade 1) In figures 1 through 5 the effects on neoplastic HeLa cells in contrast phase can be seen through the microscope. The culture was exposed to electromagnetic waves with a frequency in the megahertz range and a power of 0.25 watts for a period of about three hours. The electromagnetic energy modulated in this way brings about cytoplasmic cell fusion, which produces up to a maximum of five cells, after which cell necrosis occurs. In these figures the approach of the two cell structures, located in the center of the picture, can be seen until their fusion occurs. In figure 3 the membranes come into contact at which point the potential cell alteration can be noted (Grade 1). The above phenomenon was first noticed in 1970 and has been repeated a number of times; it was also reported at the Balkan International Congress of 1979. Cell Fusion and Necrosis (Grade 2) Figures 6 through 9 indicate the progressive fusion and necrosis in vitro of cancer cells of the CC‐178 line. These observations were conducted by the Department of Haematology and Oncology at the University of Hannover by subjecting the cells to electromagnetic waves with frequencies in the megahertz range at a power of 0.25 watts for a period of about two hours. Fig 6 Fig 8 Fig 7 Fig 9 Influence of Electromagnetic Fields on Cell Functions The preliminary observations conducted in vitro show an alteration of cell morphology, a halt to proliferation, fusion, and necrosis in lymphoblastoid cell lines, and in some neoplastic lines, after treatment with specifically modulated electromagnetic fields (HeLa, mammary carcinoma, CCL‐178, colon adenocarcinoma, H 23, H 32, h 12.1, 1411 H, testicle carcinoma, M 5, M51, stomach carcinoma, MCF‐7 human Caucasian breast adenocarcinoma ECACC 86012803, normal cell line, and MDBK bovine kidney cells) (16). It is known that cells communicate with each other by means of direct metabolic exchanges or through the transfer of ions or molecules that act as messengers. Multi‐cell signals which originate in the interaction of ligands with membrane receptors can activate a closely connected series of biochemical reactions. The biological membranes represent multi‐molecular operative structures, and even a slight alteration in the composition of the membrane can lead to significant changes in its functions. Electromagnetic fields can influence this communication between cells and within the cells themselves due to their ability to activate or change the motion of the electrical charges. In fact, an increasing amount of literature illustrates the possibility of inducing biological effects in cells when appropriate electrical and magnetic fields are applied to have a direct effect on the membranes (94,95,96). Among the various effects obtained are those on Na+ and K+ dynamics and their role in ATPasi, as well as the effects on the intermembrane exchanges of the Ca++ ion, which, because of its presence in most biomolecular processes, has earned the name of second messenger (94). Moreover, exposure conditions that have led to effects on the membrane permeability of the Ca++ ion have shown a negative influence on the mitotic fuso, and this influence is selectively tied to the characteristic of the magnetic field used. Up to now, the results obtained imply that the membrane receptors (e.g., the gluco‐protein complexes), are able to decipher electrical signals at a well defined frequency and amplitude by reacting in a specific way. The energy transformed from the electrical fields is absorbed and directly coupled to guide biochemical reactions. These results have served as the bases for some applications in the therapeutic field, particularly in the reproduction of bone tissue. (98) This is due to the fact that the activation of some cell functions is bound to electrical potentials of the on/off type, that is, not with linear but with rectangular wave shapes. Cell Fusion and Necrosis (Grade 2) The possibility that weak electric or magnetic fields can send signals past the strong potential barrier of the cytoplasmic membrane (100 KV/cm) can be explained by the hypothesis of the phenomena of resonance on certain kinds of ions (101), the co‐operative gap junction type phenomena (102, 103), and the amplification effects explained by the set up of a field gradient between the inside and outside of a spherical shell made up of three layers of dielectric properties (95). The treated cells were examined with an electron microscope that showed ultrastructural alterations in the following areas: • Cytoskeleton fiber ‐ at the structure alteration level with an increase in fibers compared to the control and with a more irregular disposition and orientation • Mitochondrion ‐ a different orientation of the mitochondrion crests and an alteration of the mitochondrion matrix which appears dishomogeneous and pycnotic compared to the control • Autophages ‐ intra‐cytoplasmic bodies in many cells Moreover, the following can be noted: • Chromatin degeneration • Thickening of the chromatin at the nuclear membrane level • Nucleus vacuolisation • Mitochondrial degeneration Electron Microscope Pictures These types of alterations, especially at the nuclear level, suggest the hypothesis that an apoptotic type of phenomenon was induced by the treatment. The characteristic of the equipment for these studies was as follows: low power (0.25 watts) electromagnetic waves with frequencies in the kilohertz range and magnetic fields and electrostatic fields specifically modulated according to the Gorgun method (GEMM: Modulated electro‐magnetic generator). Hypothesized Mechanism It is thought that the chromosomes, following the messages received as a result of the variations of potential in the cytoplasmic membrane, activate through electromechanical effects the emission of messages by the genes that regulate cell dynamics for normal cell functions or for the mitochondrial activities for ATP production. An electrical circuit composed of a zener diode attached to the base of a bipolar transistor is offered as a model for the operation of the mitochondrion. The zener diode represents the on/off pulse operation of some cell functions, the combined circuit impedance represents the impedance of the glycoproteinic sensors present on the mitochondrial membrane, and the transistor represents the ATP activation process. It is supposed that the excessive production of ATP is related to an alteration of the glycoproteinic sensors present on the mitochondrion membrane with consequent lowering of the impedance that in turn does not discriminate between the signals in frequency and activates the production of ATP in an almost continual way. The cancer cell would therefore go into mitosis due to the excess of ATP. Static magnetic fields and square wave pulsed electric fields are used to act on the mitochondrial membrane, increasing the impedance of the glycoproteinic sensors through the lengthening of the polyglycidic chain. A pulsed electromagnetic field in phase with the electrical signal is used to interfere with the communications between the genes and the protoplasmic glycoproteinic complexes involved in the promotion of cell mitosis. It is thought that the impedance of the mitochondrial membrane to the messages coming from the genes increases with the electromagnetic treatment and with increases in the malignancy (the highest impedance for undifferentiated tumours). This is related to a greater alteration of the sensors of the undifferentiated tumours and therefore to their greater predisposition to the bond with polyglycidic chains. The undifferentiated cancer cells, because of the high impedance induced on the mitochondrial membrane by the electromagnetic treatment, stop producing ATP and therefore enter into necrosis. Following the treatment the differentiated cancer cells have impedance which is still sensitive to some messages coming from the chromosomes promoting the normal production of ATP, so these cells change their state of mitosis; however, they continue to live in a quiescent state (vegetative form of life). The normal cells are not influenced by the electromagnetic treatment as the impedance of their mitochondrial sensors is not modified and remain sensitive to messages that arrive from the chromosomes for the activation of the ATP synthesis. Clinical Application Studies recently carried out reinforce the hypothesis that different classes of proteins change in response to electrical field forces induces by oscillating electric and electromagnetic fields at predetermined frequencies and intensities, and suggest that there could be biological effects that might halt the mitosis of neoplastic cells. The use of a static magnetic field of 5 mT for 50 to 60 minutes has changed the lectinici bonds of specific sites on the membrane surface of erythrocytes with a consequent alteration of the ATP content (104). The variation of the lectinici bonds is considered by the changes of the glycoproteinic complex. Pulsed square wave magnetic fields with a frequency of 10 Hz and an intensity of 10 mT on animals in vivo modified some biochemical blood parameters and produced significant effects on the erythrocyte count and the concentration of haemoglobin, calcium, and plasmatic proteins. The mechanisms of the observed effects are probably tied to the influence of the magnetic fields on the ionic permeability and capacitive reactance of the membrane due to changes in its lipid component, on the liquid crystalline structure, and on the enzymatic activity of the ionic pumps dependent on ATPasi (105). Fields of 2 KV/m with frequencies from 1 KHz up to 1 MHz activate the Na+ and K+ pumps in the ATPasi in human erythrocytes. The authors suggest that the interactions that permit the free energetic coupling between the hydrolysis of the ATP and the pumping of the ions are of the coulomb type. The results obtained indicate that only the ionic modes of transport necessary for the synthesis of the ATP for specific physiological conditions were influenced by the applied electrical field, and some types of reactions are not explicable in chemical terms but only as related to electrogenic effects (106). The use of pulsed square wave electric fields with an amplitude of 1050 volts, an impulse width of 100 microseconds, and a frequency of 1 Hz have strengthened the anti‐neoplastic effect of the bleomicina in the growth of fibro‐sarcoma SA‐1, malignant melanoma B!6, and Ehrlich ascitic tumours (EAT) (107, 108).Electromagnetic fields at a frequency of 7 MHz have been measured concomitant with cell mitosis in culture yeast cells (109). It is known that the ciclines (e.g., P16 and P21) have an important role in the processes of mitosis on cancer cells (110) The ciclines use the terso P. of the ATP. Classically this second type of interpretation has produced fundamental clinical instruments, such as, for example the electrocardiogram, the electroencephalogram, and more recently the nuclear magnetic resonance (2, 31, 32). The interest in the study of the interactions between electromagnetic fields and living Matter is placed, therefore, on three levels: • Prevention ‐ the way electromagnetic fields influence the development of illnesses (33, 47) • Diagnosis ‐ the way endogenous bio‐electric signals and weak electrical and magnetic fields, associated with bio‐molecules correlate to the state of health (11, 48, 49, 50, 51) • Treatment ‐ the way biological structures and functions can be modulated by means of electromagnetic fields (16, 17, 18, 19, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75) The following applications illustrate the therapeutic aspects: • Illnesses of the locomotor organs ‐ electromagnetic fields are used for accelerating bone regeneration especially in fractures that do not heal spontaneously and for analgesic effects. The results reported in literature relate no side effects to the treatment (62, 65, 71, 76, 77, 78). Especially noteworthy is the study of cartilage regeneration and osteoporosis. • Illnesses of the vascular apparatus ‐ excellent results are described in cases of phlebitis and related after‐effects; varicose ulcers react positively to the treatment in 90% of the cases with rare recurrences. Also obstructive arterio .pathology of the lower limbs responds well to electromagnetic treatment, showing both subjective and objective improvements (79) • Dermatological illnesses ‐both atrophic dermatitis and psoriasis respond to the treatment with satisfactory results in the latter in 60% of the cases. Bedsores can also benefit from electromagnetic treatment (79) • Surgery ‐ electromagnetic fields promote the healing of surgical wounds (79) • Inflammatory illnesses ‐ all types of acute and chronic phlogosis that were tested showed benefits from treatment with electromagnetic fields (80, 81) • Neurological illnesses ‐ positive effects were noted on neuritis irritation and on post‐herpetic neuropathologies (82) • Analgesic treatment ‐ there are numerous observations and applications of the analgesic effects of electromagnetic treatments not only in inflammatory and degenerative pathologies like arthritis, but also in neoplastic pathologies (53, 83) A growing literature proposes the use of electromagnetic energy with cancer patients. Non‐ionising electromagnetic radiation is used in the oncological field with various objectives depending on the frequency range (86, 87). Their use, besides the analgesic effects already described, can make use of the antiblastic action that can be direct or indirect, or they can be applied toward the reduction of the hiatrogenic effects of radio and chemotherapy (16, 17, 69, 87, 88). The therapeutic effects mentioned above often use the thermal effect of the induction of disorder in the target tissue; however, the major interest lies in the non‐thermal effects, which, paraphrasing Adey, might allow interventions on cell functions using the language of the cells themselves (89, 90) by means of a highly specific modulation of frequency and intensity. The characteristics of the equipment were as follows: low‐power electromagnetic waves (0.25 watt).With frequencies in the kilohertz range and specifically modulated according to the Gorgun (GEMM: Modulated Electromagnetic Generator). In Vivo Effects Modulated electromagnetic fields were applied to mice in 1974. The observations were conducted at the Marburg Universitat Klinik und Poliklinik fur‐Nuclearmedizin, Radiologiezentrum der Philippsuniversitat Marburg/Lahn at the Institute for Biophysics and Nuclear Medicine. Before being subjected to electromagnetic fields, the mice were inoculated with three different types of histopathological material: ‐ Yoshida Solid ‐ Asditis ‐ Walker A regression of the pathology was observed after the application of the electromagnetic fields. Some clinical cases are presented below, which indicate biological effects from modulated electromagnetic fields not only in cells in vitro, but also in organisms in vivo. Histopathological examinations showed that the index of proliferation decreased. Treatments were applied to patients suffering from different types of malignant neoplasia. The treatment applied was highly specific for each patient, based on the type of histopathology, the stage of the illness, and a series of personalized clinical, biophysical and environmental parameters. The electromagnetic waves used had a frequency in the kilohertz range, a power of 0.25 watts, and were applied daily for a period of time specifically determined for each case. All the studies that follow were carried out under the direction and responsibility of medical personnel. Case 1 Patient B.G., female, age 49, affected by ductile infiltrating carcinoma of the breast. After surgery and chemotherapy, metastases were noted in the axillary region. A month of treatment was performed in 1989 during which time the metastases regressed. X‐ray examinations following the treatment showed no pathological alterations. Case 2 Patient V. G., female, age 45, affected by a stomach carcinoma (adenocarcinoma slightly differentiated with ring cells and castone). Material was drawn from a voluminous sovrangular gastric ulcer, and the patient underwent a total gastrectomy. Before the therapy, metastases were present in the locoregional lymph glands, and the patient exhibited a compromised general condition. Treatment with electromagnetic energy was applied in 1988 for about forty‐five days. The metastases disappeared, and in the following check‐ups no recurrence was observed. Case 3 Patient V.A., female, age 45, affected by leiyomiosarcoma retroperitoneal that in 1984 showed a diameter of over 40cm. Before the treatment the patient complained of strong abdominal pains and generally poor health, edemas in the lower limbs due to the compression of the lower vena cava, and hydronephrosis due to uretral compression. Chemotherapy had no effect and surgery was impossible because of the adherence of the mass to vital organs, in particular the aorta. After about two months of treatment in 1987 her condition had improved and the mass seemed to have been reduced by more than half. A surgical biopsy showed fibrous muscular type cells of modest density with no cell abnormality or mitosis. In 1991 an echography showed that the volume of the mass had further reduced to about 12 to 13 cm. The mass subsequently reduced further, and in 1993 echography showed a mass diameter under 8 cm. Case 4 Patient N. M., female, age 41, had undergone a mastectomy in 1988 for infiltrating breast carcinoma followed by chemotherapy. After two years multiple bone metastases were observed in the pelvis and thigh. Figures 10 and 11 show the outcome of the X‐ray examinations before and after the treatment with electromagnetic fields in 1990 (lasting about one month). The medical report (referring to Figure 11) stated: “Compared to the last observation there are evident signs of calcifying bone repair at the endosteale and e periosteal levels. The reconstruction is apparent at the level of the right proximate metafisi, at the level of the right ischio, and corresponding to the neck of the left thigh.” Fig 10 Fig 11 Figure 10 and 11 show the x‐rays before and after the treatment. Case 5 Patient S. M., female, age 64, suffered from infiltrating ductile carcinoma of the breast. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy were performed, but the illness progressed to the presence of metastases in the axial area and in the lungs (the chest X‐ray showed small round opacities of the secondary type in both lung regions, more numerous in the lower median third right side). The treatment in 1989 with electromagnetic energy lasted two months. The metastases began to regress, although the signs in the lungs remained visible on subsequent X‐ray checks. By 1993, the pulmonary lesions had disappeared, and “no infiltrating parenchimali lesions can be observed.” A radiological inspection in 1994 confirmed this result. Case 6 Patient E. P., male, age 59, was diagnosed with pulmonary adenocarcinoma in 1988. The patient had undergone surgery with the removal of the median and lower lobes of the right lung. Subsequently extensive recurrence was observed in the right thoracic cavity and in the mediastinum (Figure 12) He suffered from a generally poor physical condition and intense thoracic pain. The clinical conditions did not permit further surgery, chemotherapy, or radiological treatments. Treatment with electromagnetic fields in 1989, which lasted approximately two months, brought about an improvement in the clinical conditions, disappearance of the pain, and reduction of the neoplastic mass. In figure 13, the thoracic x‐ray following treatment can be seen, where it is evident that there was a reduction of the mediastinic volume and expansion of the upper right pulmonary lobe. Fig 12 Fig 13 Figure 12 and 13 show the x‐ray examinations before and after the treatment. Case 7 Patient S. A., male, age 44, was diagnosed with peritoneal carcinosis in 1989, having a mass with a maximum diameter of 40 cm. An echograph report in 1990 stated: “...liver... with dishomogeneous structure due to secondary localisations, the largest of which in the left lobe has a diameter of about 4 cm.... Kidneys had moderate dilatation of the calico pieliche structures. Upper and lower abdomen was completely occupied by expansive formation of mixed structure, part liquid, part solid that compresses also the bladder and does not permit a precise evaluation of the bladder walls and the prostate.” The patient was inoperable and underwent treatment in 1990 with electromagnetic energy. The echograpy report in 1991 stated: “...the liver is enlarged with diffused dishomogeneous structure. Definite signs of nodular lesions are not identifiable at different acoustic impedances. The pelvis and partially the abdomen are occupied by a voluminous expansive formation with an maximum longitudinal diameter of approximately 20 cm., with an echostructure that is strongly dishomogeneous, referable to discariocinetic lesions. The bladder appears to have conserved regular walls. The dimensions and the echostructure of the prostate are within normal limits.” Case 8 Patient N. M., female, age 56, was diagnosed with lobular carcinoma of the breast in 1988. She underwent a surgical operation and chemotherapy. At the time of the treatment with electromagnetic energy in 1991, she was suffering from a serious decline of general health, a hepatic metastases and a costal metastases. The treatment lasted almost two months during which time the main hepatic localization reduced to a diameter of about 3 cm., and the other metastases disappeared. The upper abdominal echotomography report in 1991 stated, “an hypoechogenous area is visible, with irregular margins and a diameter of 3.3 cm. Referable, as first hypothesised, to metastases and numerous other hypoechogenous areas.” An echography report described “a delimited hypoechogenous nodular formation, with a diameter of 3 cm, of irregular shape and an endolesional hypereflectant formation.” The remaining parenchyma did not show alterations of the echogenous structure. In figure 14, a bone sintigraphy, taken in 1991, shows the examination made in 1992, in which it was pointed out, “the anomalous finding, reported in the previous examination of 28 Jan 1991 is practically no longer recognizable; the other parameters, within normal limits, have not varied.” Fig 14 Figure 14 and 15 show the x‐rays before and after the treatment. Fig 15 Case 9 Patient D. A., female age 69, was diagnosed with papillary cistoadenocarcinoma of the ovary, metastatic and infiltrating in 1987. Chemotherapy was performed, but to no avail. When the patient was subjected to electromagnetic therapy in 1990, she had metastases in the peritoneum, and the echograph showed that the “the parametrium appeared to be occupied by a voluminous mass with a diameter of about 15 cm. and mixed structure, irregular polycystic with vegetating solid formations, that were referred to ovaric adenocarcinoma.” Her general condition was seriously compromised. The treatment lasted approximately two months. The progression of the illness stopped and the mass progressively reduced in volume. The echotomograph report of November 1990 stated: “.Posterior to the uterus occupying the Douglas, ‐ an expansive formation with diameter over 12 cm. And mixed structure part liquid and part solid of probable annexial origin.” Case 10 Patient M. M., male, age 20, was diagnosed with plasmocitoma in the tibial region. The patient complained of serious pain in the tibia and was unable to walk. The tibia showed decalcification and serious bone erosion. Conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy had already been tried and no further therapeutic programs were planned. After the electromagnetic treatment performed in 1988, the pain disappeared; the patient was able to walk again, the bone recalcified and the pathological erosions disappeared. Figure 16 shows the x‐Ray before the treatment. The third radiological examination in 1989 was accompanied by the following medical analysis: “The present examination, compared to the preceding one (no. 2061) of 1 December 1988, shows that the large destructive area at the medial diaphisis, is mostly occupied by structural bone growth from bone repair under way with fixed appearance of hardened bone in formation.” The treatment consisted of approximately 25 applications. Fig 16 Fig 17 Fig 18 Figures 16 through 18 show x‐rays before, during, and after the treatment. Case 11 Patient, B. M., female, age 49, was diagnosed with carcinoma of the breast. The patient had had a mammography on May 11, 1994 (Figure 19), which indicated on the right retro‐aureolar region a nodular formation with a diameter of about 1 cm with a radiating outline. Excision was recommended. Ago‐aspiration confirmed the malignant nature of the lesion and surgery was planned for two weeks later. Waiting for the operation, the patient asked to be subjected to electromagnetic therapy and after eleven sitting the mammography was repeated. The results can be seen in Figure 20. The medical report described granulous breasts of fibromicrocystic type with no evidence of suspicious radiological character nor microcalcifications. Moreover, the cutaneous profile seemed normal. Fig 19 Fig 20 Figure 19 and 20 show the x‐rays before and after the treatment. Properties of the signals Used Most of the signals used in the clinical field of the rectangular wave shape type (99). This is due to the fact that the activation of some cell functions is bound to on/off type electrical potentials, that is not of the linear type but with waveforms of the rectangular type (100). The electromagnetic treatment last on average about twenty minutes per day with single daily sittings. The duration of the sitting is regulated by the application program and its parameters. During the first half of the treatment, the static or variable magnetic field at 50 Hz, the pulsed electric field, and the pulse electromagnetic field are all present simultaneously. In the second half, the static or variable magnetic field is not applied. The electromagnetic pulsed field and the electric pulsed field are kept in phase or in counter‐phase. The frequency of the electromagnetic field, as well as the temporal width of the square carrier wave, are fixed according to the histological type of tumour, grade of differentiation, mass, and location. BIBLIOGRAPHY Bibliography is truncated. REFERENCE LETTER DR A. H. NAGI, PAKISTAN 1977 Dr A.H. Nagi is a renown pathologist in Pakistan and is the current Chief Editor of BioMedica Journal of Pakistan Biomedical Research Society . After he reviewed several cases from tissues obtained from patients treated with GEMM in Pakistan, Dr. Nagi wrote down the following letter to a high ranking officer (perhaps the Health Minister) in Pakistan stating: Respected Gen. Iqbal, I am referring Dr. S. Gorgun who has done a pioneer work in the treatment of cancer using electrical vibrator – an equipment installed at Karachi experimentally. Sir, am writing this personal letter as I as a histopathologist found him & his subject really fascinating & needs to be demonstrated as it may be a real breakthrough. It will be nice if he could demonstrate these techniques in various institutions under your kind direction. APPLICATION LETTER DR HALUK NURBAKI TURKEY 1980 Dr Haluk Nurbaki who has been the chief physician of the Oncology Hospital in Ankara send the following letter to the Ministry of Health in Ankara requesting that he is willing to use the GEMM Device in cancer patients for pain management at his hospital. However the request has never been replied or nor the permit was granted to him. As has been recently publicized through the media, you are probably familiar with the treatment with microwaves by Dr. Seckiner Gorgun and his friends which at least shows some benefits for Cancer Treatment. Currently we are receiving several requests from himself and the media to continue his work at our hospital under our medical supervision. In case there will be no objection from your ministry, it will be at least possible to treat the patients suffering from pain. Without allowing any media speculation, we would be asking for your permission to run this study. REFERENCE LETTER PIERPAOLA PAPURELLO, ITALY 1997 The following reference letter is issued by Pierpaola Pappurello, M.D. in Torino, Italy on November 11, 1997 stating that she has personally palpated five cancer patients with palpable lesions before the first GEMM application. She attested that there was a significant reduction in the lesions when palpated right after the application. REFERENCE LETTER VALERIA BIINO, ITALY 1998 The following reference letter is issued by Valeria Biino, M.D. in Torino, Italy on January 29, 1998 stating that she has personally palpated six cancer patients with palpable lesions before the first GEMM application. She attested that there was a significant reduction in the volume of the lesions when palpated right after the application. REFERENCE LETTER PROF EMILIO DEL GIUDICE, ITALY 2001 Prof. Emilio Del Giudice is a renown Italian Nuclear Physicist, a member of the Italian National Istitute of Nuclear Physics. Together with another respected Italian Scientist Prof. Gianni Preparata they had close collaboration with Dr. Gorgun and appreciated the importance of his unique approach. Prof. Del Giudice is also the author of the key study "Magnetic Flux Quantization and Josephson Behaviour in Living Systems" that provides supportive evidence to Dr. Gorgun's theories of cellular communication. The below article is an in depth review of the GEMM Technology. Prof Emilio Del Giudice during Prof Beverly Rubik’s visit REFERENCE LETTER PROF RAFFAELE GIOVANELLI, ITALY 2001 Another respected scientist from the Medical Faculty of the University of Parma, Prof. Raffaele Giovanelli who is an electronics engineer provided an overview of the GEMM technology to Dr. Gorgun stating that he had positive results in over 90% of the cases. DR MARK NEVEU, USA 2001 In 2001 Dr Mark J. Neveu, Ph.D. a Harvard Medical School fellow and the President of National Foundation for Alternative Medicine –NFAM‐ visited Turkey with her colleagues Mrs. Annie and Mrs. Sylvia to meet with Dr Gorgun and to get more information about GEMM Therapy. After reviewing the files and talking with patients undergoing the treatment, they have decided to mention about GEMM Therapy and Dr Gorgun in the NFAM’s upcoming document Emerging Opportunity : Cancer Electromagnetic Frequency Therapy. Mark J. Neveu, at Dr Gorgun’s home in Istanbul, Turkey with Sylvia, Annie and Dr Gorgun’s wife Beyhan GUARANTEE LETTER GALILEO AVIONICA S.P.A., ITALY 2004 In Italy Dr Seckiner Gorgun worked as an independent scientific advisor to Italy’s leading Defense Electronics and Aerospace Technology company Galileo Avionica. Dr Gorgun accepted a proposal from Galileo Avionica to establish a high end Research & Development Laboratory in Istanbul to conduct contracted research for them and decided to seize the operations of his clinic in 2005 for that purpose. The following letter demonstrates Galileo Avionica’s confidence in Dr Gorgun’s competence in the electromagnetic field. Additional information is available at www.youtube.com/watch?v=NTsIQuqY6lQ INVITATION LETTER PROF JIRI POKORNY, CZECH REPUBLIC 2005 In 2005 Dr. Gorgun was invited by the Chair of the International Scientific Committee of the Coherence and Electromagnetic Fields in Biological Systems Prof Jiri Pokorny to present a lecture “Treatment of Cancer with Radio Waves without any Side Effects”. Prof Pokorny and Dr Gorgun at the Symposium INVITATION LETTER PROF GIANPIERO GERVINO, ITALY 2006 In 2006 Dr Gorgun Prof Gianpiero Gervino invited Dr Gorgun on behalf of University of Torino for a seminar to share his experiences in the field of applications of electromagnetic waves for different pathologies.