LSU Iceland 2010
Transcription
LSU Iceland 2010
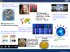
Speciality Engines How to exploit: IFL zIIP zAAP LSU Iceland 2010 © 2009 IBM Corporation Mainframe Innovation: Specialty Engines Building on a strong track record of technology innovation with specialty engines Transparent for applications when relevant IBM System z Integrated Information Processor (2006) Eligible for zIIP: System z Application Assist Processor (zAAP) 2004 Integrated Facility for Linux (IFL) 2000 Internal Coupling Facility (ICF) 1997 TLLBSUP_02 IBM System z Eligible for zAAP: Java execution environment z/OS XML System Services DB2 remote access DB2 for BI/DW ISVs IPSec encryption z/OS XML System Services z/OS Global Mirror (XRC) HiperSockets for large messages IBM GBS Scalable Architecture for Financial Reporting z/OS CIM Server DB2 sort utility zAAP on zIIP © 2009 IBM Corporation RD IBM Nordic STG Dynamic Growth in New Workloads 5000 Adoption 4000 zAAP for Java™ Based Workloads 3000 2000 1000 0 Q1 Q3 Q5 Q7 Q9 Q11 Q13 Q16 Q18 Q20 Q22 Q24 Q26 Source: IBM internal data IBM IBM 2010 2010 IBM Nordic STG IBM System z Virtualization Support , using IFLs Saving Money and Reducing Complexity Helping You “Do More with Less” with Linux Consolidate more x86 cores per CPU Spend less on software license fees Manage more virtual servers with fewer people Deploy new servers and applications faster Absorb workload spikes more easily Spend less on disaster recovery Occupy less floor space Save on energy Virtual Linux Servers z/VM Virtual Virtual Linux Linux Servers Servers z/VM z/VM Virtual Linux Servers z/VM Shared Everything Infrastructure IBM IBM 2010 2010 zAAP Concept Overview: A Simplified Example… Consider a WebSphere Application that is transactional in nature and requires 1000 MIPS today on zSeries. 80% utilization Java Execution Powered by zAAP Java Java Java 40% utilization Java Java Java Java Java 1000 MIPS for WebSphere App 500 MIPS for WebSphere App + 500 MIPS now available for additional workloads In this example, with zAAP, we can reduce the standard CP capacity requirement for the Application to 500 MIPS or a 50% reduction. * For illustrative purposes only IBM Systems IBM Nordic STG Helping to drive down the cost of IT Now even more workloads can benefit from zIIP zIIP can help to integrate data across the enterprise by optimizing resources and lowering the cost of ownership for eligible data and transaction processing workloads – Centralized data serving – First to exploit zIIP were workloads such as BI, ERP, and CRM applications running on distributed servers with remote connectivity to DB2® V8 – Network encryption – zIIP becomes an IPSec encryption engine helpful in creating highly secure connections in an enterprise – Serving XML data – zIIP is enabled for XML parsing, first to exploit this is inserting and saving DB2 9 XML data over DRDA® – Remote mirror – zIIP becomes a data mirroring engine with zIIP assisted z/OS Global Mirror function (zGM, formerly XRC) helpful in reducing server utilization at recovery site (with z/OS V1.8 and above) – Exploiting of zIIPs by ISVs zIIPs offer economics to help you – PLUS zIIP price is same for z10 EC as z9 EC and we offer no charge MES upgrades when moving to new technology le ilab Ava 07 9/ ne w ne w ! ! IBM System z10 Integrated Information Processor and IBM System z9 Integrated Information Processor IBM IBM 2010 2010 IBM Nordic STG zAAPs – not just for Java anymore! More new application technology exploiters, more new benefits zAAP designed to help implement new application technologies on System z™ – Java™ was the first exploiter – lowering the cost of computing for WebSphere® Application Server and other Java technology-based applications – z/OS XML System Services (introduced with z/OS V1.9 and rolled back to V1.8 and V1.7) helps make hosting XML data and transactions on System z more attractive. DB2 9 and Enterprise Cobol V4.1 are the first exploiters. le ilab Ava 07 9/ …. and more on Java – SDK6 on z10 EC designed to deliver improved performance over SDK5 on z9 EC – New function on z10 EC may benefit Java performance – New z10 processor chip design and more available server memory .. plus in 2Q08 – support for new decimal floating point on z10 EC by Java BigDecimal * – PLUS zAAP price is same for z10 EC as z9 EC and we offer no charge MES upgrades when moving to new technology System z = z196, z10 EC, z9 EC, z9 BC, z990, z890 IBM System z10 Application Assist Processor and IBM System z9 Application Assist Processor * All statements regarding IBM future direction and intent are subject to change or withdrawal without notice, and represents goals and objectives only. IBM IBM 2010 2010 Specialty engines z/OS LPAR WAS zAAP Application TCP/IP HiperSockets z/OS LPAR DRDA DB2 Application WAS Application not on System z TCP/IP D R D A Application Star Schema zAAP zIIP TCP/IP HiperSockets DRDA Linux on System z LPAR Application CP The IBM System z specialty engines can operate on the same machine together Shown at left, instances where zIIP can be employed with other specialty engines IFL IBM Systems How zAAPs and zIIPs are similar Both run asynchronously to general purpose processors Neither can run z/OS or be IPLed with z/OS (or any other operating system) Both receive eligible work from z/OS IBM does not impose any IBM software charges on either As of the date of this publication there are no known instances where an ISV has imposed software charges on either Both have the similar price ... Both have the same technology dividend PROJECTCPU tool can measure the eligible workload for both RMF™ monitors both zAAP and zIIP activity WLM manages both zAAP and zIIP workloads TLLBSUP_09 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation How zAAP and zIIP are different zAAP Introduced in 2004 zIIP Introduced in 2006 System z Application Assist Processor (originally System z Integrated Information Processor the zSeries Application Assist Processor) Available on System z9, System z10 servers, and Available on System z9 and System z10 servers, zEnterprise Servers ™ ® zEnterprise servers and IBM eServer zSeries 990 and 890 (z990, z890) Intended to help implement new application technologies on System z, such as Java and XML. Intended to help integrate data and transaction processing across the enterprise and on to System z9 and System z10. Exploiters include: Exploiters include: ANYTHING that uses Java via the IBM SDK (IBM Java Virtual Machine (JVM)) such as: – WebSphere Application Server – IMS™ – DB2 – CICS® – Java batch – CIM Client applications ANYTHING that uses z/OS XML System Services – DB2 9 (New Function Mode) – Enterprise COBOL V4.1 – Enterprise PL/I V3.8 – IBM XML Toolkit for z/OS, V1.9 and later – CICS TS V4.1 TLLBSUP_010 IBM System z DB2 V8 for z/OS, DB2 9, DB2 10 for z/OS – Data serving – Data Warehousing See the NEW zAAP – Select utilities on zIIP capability z/OS Communications Server – Network encryption z/OS XML System Services – DB2 9 New Function Mode z/OS Global Mirror (XRC), System Data Mover (SDM) IBM GBS Scalable Architecture for Financial Reporting HiperSockets for large messages z/OS CIM server © 2009 IBM Corporation What is DRDA? DRDA = Distributed Relational Database Architecture™ Developed by IBM Enables relational data to be distributed among multiple platforms – ‘any app to any db and any db to any db’ App or DB DB D R D A DRDA is implemented in DB2 UDB for z/OS V8 and reduces the need for additional gateway products that may affect performance and availability. The Open Group adopted DRDA in 1998 as the open standard for database access interoperability. An application uses DRDA application requestor or server to access a remote database. DB2 Connect is an example of a DRDA application server. The universal driver is an example of a DRDA application requester DRDA is network independent. It can use TCP/IP or SNA as a network protocol to flow DRDA commands. Connections using SNA are not eligible for zIIP. So.... regarding the zIIP: If DB2 for z/OS V8 work load comes over TCP/IP and is DRDA compliant (and not stored procedures or user-defined functions), a portion of that DB2 workload is eligible to be redirected to the zIIP – you need BOTH TCP/IP and DRDA but not stored procedures or user-defined functions. IBM Systems What is Star Schema? DB2 V8 zIIP redirect enabling APAR : PK19921 for Star Schema Star schema = a relational database schema for representing multidimensional data Sometimes graphically represented as a ‘star’ Data stored in a central fact table Surrounded by additional dimension tables holding information on each perspective of the data Example: store "facts" of the sale (units sold, price, ..) with product, time, customer, and store keys in a central fact table. Store full descriptive detail for each keys in surrounding dimension tables. This allows you to avoid redundantly storing this information (such as product description) for each individual transaction Complex star schema parallel queries include the acts of joining several dimensions of a star schema data set (like promotion vs. product). So.... regarding zIIP: if the workload uses DB2 UDB for z/OS V8 to join star schemas, then portions of that DB2 workload will be eligible to be redirected to the zIIP. IBM Systems What is index maintenance? An index allows quick access to the rows in a table. Indexes are created using one or more columns of a table. Over time, as data in a large database is manipulated indexes can become less efficient. They need to be updated and maintained. This can be a very big task. LOAD – loads your tables REORG – improves your index performance REBUILD INDEX – creates or rebuilds your indexes So.... regarding the zIIP: The BUILD phase of LOAD, REORG, and REBUILD utilities performs index maintenance. Most of the BUILD phase is eligible to be redirected to the zIIP. DB2 V8 zIIP redirect enabling APAR : PK19920 for Utilities IBM Systems IBM Nordic STG IBM IBM 2010 2010 IBM Nordic STG IBM IBM 2010 2010 Tool for zIIP sizing analysis CP2KEXTR tool – IBM rep. sends the tools with instructions – z/OS V1.8 and higher, DB2 V8 or higher – PROJECTCPU=YES in IEAOPT member – Collects data from SMF types 70, 71, 72, 73 ,74, 75 and 78 (from a week or more) – Produces a EDF file as output – Run by customer zCP3000 IBM tool – Uses the EDF file as input – Produces an Analysis Report – Run by IBM IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation zIIP Analysis using zCP3000 (sample) The CP graph shows the utilization for an average 4.0 CPs. (The input had an average of 4.0 CPs.) The zIIP graph shows the utilization for an average 0.0 zIIPs. (The input had an average of 0.0 zIIPs.) These graphs are based on a 2094-704 processor, and a suggested zIIP utilization threshold of 100%. When there's potential zIIP time but no zIIPs defined, the potential zIIP time is displayed as if there were 1 zIIP. In this case the maximum zIIP (actual plus potential) is 40.4% of a single zIIP. This peak occurred at 10:00 on 24/11/08. IBM Systems IBM Nordic STG The value of zAAP and zIIP ? 1. Offload a WebSphere Application that is transactional in nature and requires 1000 MIPS today on System z 2. Add a WAS workload from a Distributed Server Java execution powered by a zAAP 80% utilization CP CP System z JAVA DB2 JAVA EJB Server System z EJB DB2 JAVA zAAP System z NO SW COST 40% utilization EJB JAVA Server System z JAVA EJB DB2 DB2 JAVA 1000 MIPS for WebSphere App 500 MIPS for WebSphere App + 500 MIPS now available for additional workloads 1. Reduction of the standard CP capacity requirement for the application to 500 MIPS or a 50% reduction.* 2. Or it is possible to add the JAVA work without affection the cost of the current workload and for NO SW cost IBM IBM 2010 2010 System z Specialty Engines – Update TLLBSUP_019 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation zAAPs and zIIPs – Designed to help implement, integrate, optimize new technologies Enabled technologies, in order of introduction: Java – for WebSphere® Application Server and Java technology-based applications Centralized data serving eligible for zIIP – Portions of BI, ERP, and CRM remote connectivity to DB2 V8, as well as portions of long running parallel queries. and select utilities. Network encryption on zIIP – IPSec network encryption/ decryption (with z/OS V1.8) XML parsing – z/OS XML System Services eligible on zAAP or zIIP (with z/OS V1.9, V1.8 and V1.7 with maint.) Remote mirror – zIIP assisted z/OS Global Mirror function (with z/OS V1.9) HiperSockets – HiperSockets Multiple Write operation for outbound large messages (with z/OS V1.9) Business Intelligence – IBM Scalable Architecture for Financial Reporting provides a highvolume, high performance reporting – can be eligible for zIIP Intra-server communications – z/OS CIM Server processing eligible for zIIP (with z/OS V1.11). DB2 sort utility – DB2 utilities sorting fixed-length records using IBM's memory object sorting technique zAAP on zIIP capability – Optimize the purchase of a new zIIP or maximize your investment in existing zIIPs TLLBSUP_020 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation RMF: zAAP and zIIP support RMF supports zAAP and zIIP processors by extending the – Postprocessor CPU activity report – Postprocessor Workload report – Monitor III Enclave report In detail... – RMF distinguishes between standard CP, zAAP, and zIIP where necessary – Collects and reports about zAAP and zIIP service times – Collects and reports about zAAP and zIIP usage and delay states for service and report class periods Following SMF record types are extended – – – – SMF record 70 subtype 1 (CPU activity) SMF record 72 subtype 3 (Workload activity) SMF record 79 subtype 1 and 2 (Address Space State and Resource data) SMF record 30 (provides more detail on address spaces) Review and modify any user-written programs, if affected TLLBSUP_021 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation Large Systems Update 2009 International Technical Support Organization for ITD Global The Power and Flexibility of System z Virtualization Over 40 years of continuous innovation in virtualization technologies Multiple images concurrently share all physical resources Resources delivered as required, automatically, based on business-oriented goals New OS images can be started without affecting ongoing work Hardware assists used to accelerate virtualization operations (e.g., SIE) ! "# " z/OS Linux Linux % ! & % ! & Linux Linux Linux $ ' " z/OS z/OS z/OS z/OS z/VM Linux Linux z/VM LPAR 1 LPAR 2 LPAR 3 LPAR 4 LPAR 5 LPAR 6 LPAR 7 LPAR 8 CP CP CP CP CP CP zAAP zAAP zIIP zIIP IFL © 2009 IBM Corporation IFL IFL IFL IFL IFL IFL IFL zAAP on zIIP Capability TLLBSUP_023 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation What is the zAAP on zIIP capability? A new capability that can enable System z Application Assist Processor (zAAP) eligible workloads to run on System z Integrated Information Processors (zIIPs) – Ideal for customers with no zAAPs and zIIPs • The combined eligible workloads may make the acquisition of a single zIIP cost effective. – Ideal for customers with only zIIP processors • Makes Java and z/OS XML System Services-based workloads eligible to run on existing zIIPs – maximizes zIIP investment. – Available September 25, 2009 with z/OS V1.11 and z/OS V1.9 and V1.10 (with PTF) • This new capability is not available for z/OS LPARS if zAAPs are installed on the server. TLLBSUP_024 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation Example 1: zAAP on zIIP** Can enable you to run zIIP- and zAAP-eligible workloads on the zIIP. CPs only, NO zAAPs and zIIPs White space All workloads on general purpose processors ZAAPZIIP=YES Small amount of zIIP and zAAP eligible work CPs – Optimize the purchase of a new zIIP The potential to run any of these workloads on your new zIIP White space General purpose workload CPs zIIP ** For illustrative purposes only, your results will vary. This new capability is not available for z/OS LPARS if zAAPs are installed on the server TLLBSUP_025 IBM System z ANYTHING that uses Java via the IBM SDK (IBM Java Virtual Machine (JVM)) such as: – WebSphere Application Server – IMS – DB2 – CICS – Java batch – CIM Client applications ANYTHING that uses z/OS XML System Services – DB2 9 (New Function Mode) – Enterprise COBOL V4.1 – Enterprise PL/I V3.8 – IBM XML Toolkit for z/OS, V1.9 and later – CICS TS V4.1 DB2 V8 for z/OS, DB2 9 for z/OS – Data serving – Data Warehousing – Select utilities z/OS Communications Server – Network encryption – HiperSockets for large messages z/OS CIM server ISV workloads © 2009 IBM Corporation Example 2: zAAP on zIIP** Can enable you to run zIIP- and zAAP-eligible workloads on the zIIP. – Maximize your investment in existing zIIPs. CPs and zIIPs White space Potentially add the following workloads to your existing zIIPs White space General purpose workload ZAAPZIIP=YES Small amount zAAP eligible work CPs zIIPs General purpose worload CPs zIIP ANYTHING that uses Java via the IBM SDK (IBM Java Virtual Machine (JVM)) such as: – WebSphere Application Server – IMS – DB2 – CICS – Java batch – CIM Client applications ANYTHING that uses z/OS XML System Services – DB2 9 (New Function Mode) – Enterprise COBOL V4.1 – Enterprise PL/I V3.8 – IBM XML Toolkit for z/OS – CICS TS V4.1 ** For illustrative purposes only, your results will vary. This new capability is not available for z/OS LPARS if zAAPs are installed on the server TLLBSUP_026 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation How to enable the zAAP on zIIP capability The capability ships default enabled with z/OS V1.11. – Parameter in IEASYSxx : ZAAPZIIP = YES (default in z/OS V1.11) – If you wish to disable the function for any reason, you must IPL with ZAAPZIIP=NO in the IEASYSxx Parmlib member Also available with z/OS V1.9 and V1.10 – With PTF for APAR OA27495 – Enabled with ZAAPZIIP=YES in the IEASYSxx Parmlib (the default is NO) This new capability does not remove the requirement to purchase and maintain one or more general purpose processors for every zIIP processor on the server – This part of the IBM terms and conditions surrounding the IBM System z specialty engines is unchanged. TLLBSUP_027 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation zAAP on zIIP Requirements – System z9 or z10 • With zIIP(s) and no zAAP(s) • one or more general purpose processors for every zIIP processor on the server – Available on z/OS V1.11, and z/OS 1.9 and 1.10 (with PTF for APAR OA27495) – New ZZ system parameter • ZAAPZIIP=YES or NO (or ZZ=YES or NO) • For z/OS 1.11 default = YES (enabled) • For z/OS 1.9 and 1.10 default = NO (not enabled) • If zAAPs are on the server, the zAAP on zIIP capability will not be honored For more information: – The zIIP and zAAP Web sites at: ibm.com/systems/z/advantages/specialtyengines/index.html – The zAAP on zIIP capability (and ZZ system parameter) is described in z/OS V1R11.0 MVS Initialization and Tuning Reference (SA22-7592-18) TLLBSUP_028 IBM System z © 2009 IBM Corporation For more information zIIPs http://www-03.ibm.com/systems/z/hardware/features/ziip/resources.html FAQ, Getting started, sizing information, whitepapers zAAPs http://www-03.ibm.com/systems/z/hardware/features/zaap/resources.html FAQ, Getting started, sizing information, whitepapers IFLs http://www-03.ibm.com/systems/z/os/linux/ FAQ, Whitepapers, Tuning hints and tips IBM Systems Questions What About...... IBM Systems