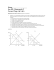Econ 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Sample Exam 1
Transcription
Econ 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Sample Exam 1
Econ 2106 Principles of Microeconomics Sample Exam 1 ____ 1. Demand is said to be elastic if a. the price of the good responds substantially to changes in demand. b. demand shifts substantially when the price of the good changes. c. buyers do not respond much to changes in the price of the good. d. the quantity demanded responds substantially to changes in the price of the good. ____ 2. If a person only occasionally enjoys a cup of coffee, his demand for coffee would be a. horizontal. b. inelastic. c. unit elastic. d. elastic. ____ 3. When the price of bubble gum is $0.50, the quantity demanded is 400 packs per day. When the price falls to $0.40, the quantity demanded increases to 600. Given this information and using the midpoint method, you know that the demand for bubble gum is a. inelastic. b. elastic. c. unit elastic. d. perfectly inelastic. ____ 4. Suppose the price of Twinkies is reduced from $1.45 to $1.25 and, as a result, the quantity of Twinkies demanded increases from 2,000 to 2,200. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand for Twinkies in the given price range is a. 2.00. b. 1.55. c. 1.00. d. .64. ____ 5. When the local used bookstore prices economics books at $15.00 each, they generally sell 70 per month. If they lower the price to $7.00 each they sell 90. Given this, we know that the elasticity of demand for economics books is a. 2.91, so this store should lower price to raise total revenue. b. 2.91, so this store should raise price to raise total revenue. c. 0.34, so this store should lower price to raise total revenue. d. 0.34, so this store should raise price to raise total revenue. ____ 6. Which of the following would have the most elastic demand? a. clothing b. blue jeans c. Levi jeans d. All three would have the same elasticity of demand since they are all related. 1 ____ 7. When demand is elastic in the current price range, a. an increase in price would increase total revenue because the decrease in quantity demanded is less than the increase in price. b. an increase in price would decrease total revenue because the decrease in quantity demanded is greater than the increase in price. c. a decrease in price would decrease total revenue because the increase in quantity demanded is smaller than the decrease in price. d. a decrease in price would not affect the total revenue. ____ 8. If a change in the price of a good results in no change in total revenue, a. the demand for the good must be elastic. b. the demand for the good must be inelastic. c. the demand for the good must be unit elastic. d. buyers must not respond very much to a change in price. ____ 9. You and your college roommate eat three packages of Ramen noodles each week. After graduation last month, both of you were hired at several times your college income. You still enjoy Ramen noodles very much and buy even more, but your roommate plans to buy other foods she prefers more. When looking at income elasticity of demand for Ramen noodles, yours would a. be negative and your roommate's would be positive. b. be positive and your roommate's would be negative. c. be zero and your roommate's would approach infinity. d. approach infinity and your roommate's would be zero. ____ 10. Get Smart University is contemplating increasing tuition to enhance revenue. If GSU feels that raising tuition would enhance revenue, they are a. necessarily ignoring the law of demand. b. assuming that the demand for university education is elastic. c. assuming that the demand for university education is inelastic. d. assuming that the supply of university education is elastic. ____ 11. Holding all else constant, if a pencil manufacturer increases production by 20 percent when the market price of pencils increases from $0.50 to $0.60, then the price elasticity of supply, using the midpoint method, must be a. elastic, since elasticity is equal to 1.11. b. inelastic, since elasticity is equal to 1.11. c. inelastic, since elasticity is equal to .90. d. elastic, since elasticity is equal to .90. ____ 12. If the elasticity of supply is zero, then a. supply is very elastic. b. the supply curve is horizontal. c. the quantity supplied is the same regardless of price. d. Both b and c are correct. ____ 13. If wheat farmers know that the demand for wheat is inelastic, and they want to increase their total revenue, they should all a. plant more wheat so that they would be able to sell more each year. b. increase spending on fertilizer in an attempt to produce more on the acres they farm. c. reduce the number of acres they plant in wheat. d. use better machinery. 2 ____ 14. Given the market for illegal drugs, if the government attempts to reduce the flow of drugs into the United States, a. supply would fall and prices would rise. b. demand would fall and prices would fall also. c. demand and supply would both fall, leaving prices basically the same. d. supply may fall, but demand would increase, causing prices to skyrocket. ____ 15. Suppose a producer is able to separate customers into two groups, one having a price inelastic demand and the other having a price elastic demand. If the producer's objective is to increase total revenue, she should a. increase the price charged to customers with the price elastic demand and decrease the price charged to customers with the price inelastic demand. b. decrease the price charged to customers with the price elastic demand and increase the price charged to customers with the price inelastic demand. c. charge the same price to both groups of customers. d. increase the price for both groups of customers. ____ 16. Price controls are a. used to make markets more efficient. b. usually enacted when policymakers believe that the market price of a good or service is unfair to buyers or sellers. c. nearly always effective in eliminating inequities. d. established by firms with monopoly power. ____ 17. A price ceiling will only be binding if it is set a. equal to equilibrium price. b. above equilibrium price. c. below equilibrium price. d. A price ceiling is never binding in a free market system. ____ 18. With a binding price floor the market price will a. be lower than the price floor. b. be higher than the price floor. c. equal the price floor. d. It is impossible to compare the market price with the price floor. ____ 19. When binding price ceilings are imposed in a market a. price no longer serves as a rationing device. b. the market will be cleared of any shortages or surpluses that existed previously. c. buyers and sellers both benefit equally. d. the government is attempting to improve market efficiency. ____ 20. Price ceilings and price floors a. are desirable because they make markets more efficient as well as equitable. b. cause surpluses and shortages to persist since price cannot adjust to the market equilibrium price. c. can be enacted to restore a market to equilibrium. d. are imposed because they can make the poor in the economy better off without causing adverse effects. 3 ____ 211. A minimu um wage imp posed above a market's equ uilibrium wag ge will result in the quantity a. suppllied of labor being b greater than the quan ntity demand ded of labor an nd unemploy yment will occur. o b. demaanded of laborr being greateer than the qu uantity suppliied of labor an nd unemploy yment will occur. o c. suppllied of labor being b greater than the quan ntity demand ded of labor an nd a shortagee of workeers will occurr. d. demaanded of laborr being greateer than the qu uantity suppliied of labor an nd a shortagee of workeers will occurr. ____ 222. Which of the following g is NOT a fun nction of pricces in a markeet system? ucial job of balancing supply and deman nd. a. Pricess have the cru b. Pricess send signalss to buyers an nd sellers to help h them mak ke rational economic decissions. c. Pricess coordinate economic e activity. d. Pricess make an equ uitable distrib bution of good ds and services among con nsumers posssible. Figure 6-88 ____ 233. Refer to Figure F 6-8. Th he price buyerrs will pay aftter the tax is imposed i is a. $8.00.. b. $6.00.. c. $5.00.. d. $3.00.. ____ 244. A tax on the t buyers of coffee will a. reducce the equilibrrium price of coffee, and in ncrease the eq quilibrium qu uantity. b. increaase the equilib brium price of o coffee, and reduce the eq quilibrium qu uantity. c. increaase the equilib brium price of o coffee, and increase the equilibrium e q quantity. d. reducce the equilibrrium price of coffee, and reeduce the equ uilibrium quaantity. Figure 6-111 ____ 255. Refer to Figure F 6-11. In n which mark ket will the majority m of a taax be paid by the seller? a. markeet (a) b. markeet (b) c. markeet (c) d. All off the above are correct. 4 ____ 266. Which of the following g is the MOST T likely to resu ult from the imposition of a price floor in the markett for rental cars? g given n to people as an incentive to a rent car a. free gasoline b. poor engine e maintenance in ren ntal cars c. an acccumulation of dirt on the interior i of ren ntal cars d. slow replacement r of o old rental cars c with new w ones ____ 277. Suppose there t is an earrly freeze in California C thaat ruins the lem mon crop. Wh hat happens to consumer surplus in thee market fo or lemons? a. It incrreases. b. It decreases. n affected by y this change in market forrces. c. It is not d. It incrreases very brriefly then decreases. yers' willingn ness to pay forr a case of Van nilla Coke. This tablee refers to fivee possible buy Table 7-2 BUYER WILLINGNESS S TO PAY DAVID $8.5 50 LAURA $7.0 00 MEGAN N $5.5 50 MALLOR RY $4.0 00 AUDREY Y $3.5 50 ____ 288. Refer to Table T 7-2. If th he market priice is $5.50, th he consumer surplus s in thee market will be a. $3.00.. b. $4.50.. c. $15.500. d. $21.000. ____ 299. If the costt of producing g sofas decreaases, consumeer surplus willl a. increaase, then decrrease. b. decrease. c. remaiin constant. d. increaase. Figure 7-11 ____ 300. Refer to Figure F 7-1. Arrea C represen nts a. the deecrease in con nsumer surplu us that resultss from a dow wnward-slopin ng demand cu urve. b. consu umer surplus to new consu umers who en nter the markeet when the price p falls from m P2 to P1 . ducer surpluss when quantiity sold increaases from Q2 to Q1 . c. an inccrease in prod d. a decrrease in consu umer surplus to each consu umer in the market. m 5 ____ 31. The Surgeon General announces that eating chocolate increases tooth decay. As a result, the equilibrium market price of chocolate a. increases, and producer surplus increases. b. increases, and producer surplus decreases. c. decreases, and producer surplus decreases. d. decreases, and producer surplus increases. The following table represents the costs of five possible sellers. Table 7-3 SELLER COST DALE $1,500 JILL $1,200 DENISE $1,000 CATHERINE $750 JACKSON $500 ____ 32. Refer to Table 7-3. If the market price is $1,000, the total cost in the market would be a. $3,700. b. $2,700. c. $2,250. d. $1,500. ____ 33. Total surplus in a market is represented by the total area a. under the demand curve and above the price. b. above the supply curve and up to the equilibrium price. c. under price and up to the point of equilibrium. d. between the demand and supply curves up to the point of equilibrium. ____ 34. Inefficiency exists in any economy when a good is a. not being consumed by buyers who value it most highly. b. not distributed fairly among buyers. c. not being produced by the highest-cost producer. d. being produced with less than all available resources. ____ 35. If a market is allowed to move freely to its equilibrium price and quantity, then an increase in supply will a. increase consumer surplus. b. reduce consumer surplus. c. not affect consumer surplus. d. possibly increase, decrease or not affect consumer surplus. ____ 36. If there are no externalities, the "invisible hand" leads a market to maximize a. producer profit from that market. b. total benefit to society from that market. c. both equity and efficiency in that market. d. output of goods or services in that market. ____ 37. Dioxin emission that results from the production of paper is a good example of a negative externality because a. self-interested paper firms are generally unaware of environmental regulations. b. there are fines for producing too much dioxin. c. self-interested paper producers will not consider the full cost of the dioxin pollution they create. d. toxic emissions are the only form of an externality. 6 ____ 388. When thee government intervenes in n markets witth externalitiees it does so to o a. increaase productio on when negative externaliities are preseent. b. protecct interests off bystanders. c. make certain all beenefits are recceived by marrket participants. d. betterr coordinate th he action of buyers b and sellers. ____ 399. A positivee externality a. causes the productt to be overprroduced. t market participants. b. provides an additional benefit to wer equilibriu um price. c. benefits consumerss because it reesults in a low arket bystandeer. d. is a beenefit to a ma ____ 400. When neg gative externa alities are present in a mark ket a. privatte costs will be b greater than n social costs. b. sociall costs will be greater than private costs. c. goverrnment regula ation to resolv ve the problem m is always necessary. n d. the market m will nott be able to reeach any equiilibrium situaation. ____ 411. Which of the following g statements is i most correcct about a marrket which is characterized d by a negativ ve production n y? externality a. The equilibrium qu uantity of outtput is equal to t the socially y optimal quaantity. uantity of outtput is greaterr than the soccially optimal quantity. b. The equilibrium qu vention is nott required to achieve a a sociially optimal quantity of ou utput. c. Goverrnment interv d. The co ost to the pro oducer exceed ds the cost to society. s ____ 422. Which of the following g statements about a internalizing a negattive externalitty is most corrrect? nalizing a neg gative externaality will causse an industry y to decrease the t quantity it i a. Intern suppllies to the marrket and decrrease the pricee of the good produced. b. Intern nalizing a neg gative externaality will causse an industry y to decrease the t quantity it i suppllies to the marrket and increease the pricee of the good produced. p c. Intern nalizing a neg gative externaality will causse an industry y to increase the t quantity itt suppllies to the marrket and decrrease the pricee of the good produced. d. Intern nalizing a neg gative externaality will causse an industry y to increase the t quantity itt suppllies to the marrket and increease the pricee of the good produced. p Figure 10--6 ____ 433. Refer to Figure F 10-6. To T internalize the externalitty in this marrket the goverrnment should a. imposse a tax on thiis product. b. provide a subsidy for this produ uct. urage firms to o supply moree of this produ uct by offerin ng tax incentiv ves. c. encou d. produ uce the produ uct itself. 7 ____ 444. Dick own ns a dog whosse barking ann noys Dick's neighbor n Jane.. Suppose thaat the benefit of o owning thee dog is worth $5000 to Dick and d that Jane beears a cost of $700 $ from thee barking. Asssuming Dick has h the legal right to keep the dog, a possible priv vate solution to this probleem is that a. Jane pays p Dick $50 00 to get rid of the dog. b. Dick pays p Jane $65 50 for her inco onvenience. c. Jane pays p Dick $65 50 to get rid of the dog. d. Theree is no privatee solution thatt would imprrove this situaation. ____ 455. Assume th hat your room mmate, Vanesssa, is very messy, m and acccording to cam mpus policy, you y have a right to live in an unclutttered apartment. Suppose she gets a $200 benefit fro om being messy but imposes a $100 costt on you. The Coase theeorem would suggest that an a efficient so olution would d be for your roommate to a. stop her h messy hab bits or else mo ove out. b. pay you y at least $100 but less th han $200 to liv ve with the clu utter. c. contin nue to be messsy and force you to make other living arrangements a s elsewhere. d. demaand payment of o at least $1000 but no morre than $200 to clean up aftter herself. ____ 466. In Singapore, littering fines f are stricctly enforced. This is an exaample of a po olicy hich moral cod des and social sanctions reeduce the polllution externaality. a. in wh b. that reelies on the Coase C Theorem m. c. that discriminates d against foreig gners. d. in wh hich private in ncentives are used to reducce the pollutio on externality y in Singaporee. ____ 477. Emission controls on automobiles a are an example of a a. Pigov vian tax on au utomobiles, baased on how much m they po ollute. b. comm mand-and-con ntrol policy to o increase sociial efficiency. c. policy y that reducess pollution by y allocating reesources throu ugh market mechanisms. d. policy y to reduce co ongestion on urban u freewaays. Figure 10--8 ____ 488. Refer to Figure F 10-8. Which W curve best b representts a Pigovian tax? a. A b. B c. C d. D ____ 499. The differrence between n a Pigovian tax t and pollution permits is i a. a Pigo ovian tax sets the price of pollution p and d permits set the t quantity of o pollution. b. a Pigo ovian tax prov vides a more efficient outccome than perrmits. c. a Pigo ovian tax sets the quantity of pollution and a permits set s the price of o pollution. d. permiits provide a more efficien nt outcome thaan a Pigovian n tax. ____ 500. Tradable pollution p perrmits a. pricess are set by th he governmen nt. b. will be b bought by firms f which can c reduce po ollution only at a high costs. c. are lik kely to create a higher leveel of total polllution. d. are less desirable th han Pigovian n taxes in redu ucing pollutio on. 8 ____ 51. A good is excludable if a. one person's use of the good diminishes another person's enjoyment of it. b. the government can regulate its availability. c. it is not a normal good. d. people can be prevented from using it. ____ 52. Goods that are rival include both a. natural monopolies and public goods. b. public goods and common resources. c. common resources and private goods. d. private goods and natural monopolies. ____ 53. When one person uses a common resource, which will NOT occur? a. An externality will arise. b. Other people are worse off. c. It is difficult to charge him or her for usage of it. d. No one else will be able to use the common resource. ____ 54. National defense is provided by the government because a. it is impossible for private markets to produce public goods. b. products provided by the government can be produced more efficiently. c. free-riders make it difficult for private markets to supply the socially optimal quantity. d. if the good were produced in private markets, most likely too much of the product would be produced. ____ 55. Market failure associated with the free-rider problem is a result of a. a problem associated with pollution. b. benefits that accrue to those who don't pay. c. losses that accrue to providers of the product. d. a project in which costs exceed benefits. ____ 56. When an infinite value is placed on human life, policymakers who rely on cost-benefit analysis a. are forced to pursue any project in which a single human life is saved. b. are likely to make decisions that optimally allocate society's scarce resources. c. would not pursue any public project that would not save human life. d. would be forced to rely on private markets to provide the project. ____ 57. Suppose that you want to put on a fireworks display in your hometown of 1,000 people this July. The cost of the display is $6,000 and each person values the display at $5. After a month, you have only sold 50 tickets at $5 each. The result is a. the local government will put on the display but you will not. b. you will still put on the display but the local government would not. c. neither you nor the local government would put on the display. d. This question cannot be answered without knowing the amount of tax the local government would charge for the display. ____ 58. The Tragedy of the Commons can be corrected by a. providing more of the resource for public use. b. assigning property rights to individuals. c. providing government subsidies for the resource. d. making certain everyone in the economy has access to the resource. 9 ____ 59. Proposals to use road tolls in an effort to reduce traffic congestion are often rejected by the public because a. there is no longer sufficient government intervention. b. they allow the rich to drive more than the poor. c. they tax only those who chose to drive on the toll roads. d. All of the above are correct. ____ 60. Four friends who love to ski decide to pool their financial resources and equally share the cost of a one-week time-share condominium in Alta, Utah. Unfortunately the condominium does not come with maid service. Everyone values clean dishes, but the fact that unwashed dishes pile up in the sink would best be explained by an economist who understands that clean dishes in the cupboard reflect a. a common resource problem. b. a problem similar to cost-benefit analysis for public projects. c. household behavior of the invisible hand. d. All of the above are correct. Answer Key 1. D 2. D 3. B 4. D 5. D 6. C 7. B 8. C 9. B 10. C 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. A 15. B 16. B 17. C 18. A 19. A 20. B 21. A 22. D 23. A 24. D 25. A 26. A 27. B 28. B 29. D 30. B 10 31. C 32. C 33. D 34. A 35. A 36. B 37. C 38. B 39. D 40. B 41. B 42. B 43. A 44. A 45. B 46. A 47. B 48. A 49. A 50. B 51. D 52. C 53. D 54. C 55. B 56. A 57. C 58. B 59. B 60. A 11