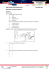Pipe Cleaner Babies
Transcription
Pipe Cleaner Babies
Name: __________________________ Pipe Cleaner Babies In this activity you will play the role of a parent, your lab partner will play the role of the other parent. You will use chromosome and gene models to create an offspring. You will then use class data to determine how accurate Punnett squares are by comparing probability to what is actually seen in a population. Step 1: How to Use the Model: You will receive a baggie with pipe cleaners and beads. The pipe cleaners represent chromosomes and the beads represent genes located on the chromosomes. In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes, 23 from their mom and 23 from their dad. This means that humans have a total of 46 chromosomes in each of their cells. Humans have thousands of different genes, but for this exercise, we will only focus on a few. When you get your bag, you will notice that you have four white and two colored pipe cleaners. If you have two pink chromosomes, you are to play the role of female (XX). If you have one pink and one blue, you are to play the role of the male (XY). You will not earn your chromosomes until you answer the following questions and show the teacher. 1. What do the pipe cleaners represent? ___________________________________ 2. What do the beads represent? ______________________ 3. 4. Humans have ___________ pairs of chromosomes. How many is that total? ___________ If you have two pink pipe cleaners, you are playing the role of _________________ 5. If you are the mom what is your genotype? _______ 6. If you have a pink and a blue pip cleaner, you are playing the role of _________________ 7. If you are the dad what is your genotype? _______ 8. The blue pipe cleaner represents the _________ chromosome. Before you start, please make sure that you have the correct combination of pipe cleaners in your bag!!!! This is what you should see: Step 2: Figure out the parents traits: Remove the chromosomes from the bag, but make sure you do NOT mix up you and your partner's chromosomes!!! Arrange the chromosomes in order of size, you should have: Two long white pipe cleaners Two shorter pipe cleaners Two colored pipe cleaners. The white pairs represent HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES. 9. What are homologous chromosomes? (look it up!) ______________________________________________________________________________ The colored pairs represent SEX CHROMOSOMES 10. What are sex chromosomes? (look it up!) ______________________________________________________________________________ HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES Eye Color Hair Color (longer white pipe cleaners) (shorter white pipe cleaners) Brown/Orange bead represents the dominant gene (B) - brown Blue bead represents the recessive gene (b) - blue Red bead represents the dominant gene (D)- dark White bead represents the recessive gene (d) - blonde BB = brown eyes | Bb = brown eyes | bb = blue eyes DD= dark hair | Dd = dark hair | dd = blonde hair What is her genotype? ___ ___ (what color beads?) What is her phenotype? What color eyes? _____________ What is her genotype? ___ ____ (what color beads?) What is her phenotype? What color hair? _____________ What is his genotype? ____ ____(what color beads?) What is his phenotype? What color eyes? _____________ What is his genotype? ____ ____(what color beads?) What is his phenotype? What color hair? _____________ What is the probability for each eye color in their offspring? What is the probability for each hair color in their offspring? Brown? = _______% Dark? = _______% Blue? = ________% Blonde? = ________% SEX CHROMOSOMES Hemophilia (colored pipe cleaners) Purple bead represents the dominant gene (H) -- normal Clear bead represents the recessive gene (h) – hemophiliac X__ **In girls** XHXH = normal | XHXh = normal (carrier) | XhXh = hemophiliac **In boys** XHY = normal | XhY = hemophiliac What is mom's genotype? ___ ___ What is mom’s phenotype (Is she a carrier?) ___________ Y__ X__ X__ What is dad's genotype? ___ ___ What is dad’s phenotype (Is he a carrier?) __________ Why doesn't dad get two alleles for this trait? ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ Because this is a sex linked trait, the Punnett square is going to look a little different! Step 3: Time to Start Your Family 1. The dad places one set of the homologous pairs of chromosomes (longer set of pipe cleaners) behind his back, with a chromosome (pipe cleaner) in each hand. The mom picks the hand she wants for the child. Lay this chromosome on the table in front of you and set the other aside (out of the way). 2. Repeat this procedure for the other homologous pair (shorter set) and for the sex chromosomes (colored set). **It’s should be noted that if the blue chromosome gets chosen from the sex chromosomes, the child in this cross is going to be a boy. 3. Now the mom does the same process. “She” can start by placing one set of the homologous pairs behind her back and the male chooses, and then repeat with the remaining chromosome pairs. 4. The chromosomes chosen and set on the table in front of you are the genes your first child will receive! Step 4: Determine the Traits of Your First Child Arrange the chromosomes into homologous pairs (2 long, 2 short, 2 colored) and figure out what phenotypes (appearance or observable trait) the offspring has. What is the child’s genotype for gender? ___ ___ Phenotype? _______________ What is the child’s genotype for eye color? ___ ___ Phenotype?______________ What is the child’s genotype for hair color? ___ ___ Phenotype?_____________ Is the child’s genotype for hemophilia? ___ ___ Phenotype? ________________ Step 5: Data Table (Hemophiliac, Normal, or Carrier) Go to the last page for the class data table, your group is group # _______ . When you are finished, you will post your data on the board. Other groups will also post their children's data. Fill out the entire chart to find out the traits of the new generation of children. **Please make sure you have the right chromosomes in the right bags when you return them!! Individual Group Data Eye Color Hair Color Sex Hemophilia Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6 Group 7 Group 8 Group 9 Group 10 Group 11 Group 12 Group 13 Group 14 Group 15 Group 16 Complete Class Data # of Babies with trait Total Number of Babies Total Number of Girls Total Number of Boys # of Babies with Brown Eyes # of Babies with Blue Eyes # of Babies with Dark Hair # of Babies with Blonde Hair # of Girls with Hemophilia # of Boys with Hemophilia Percentages Step 6: Analysis Directions: Using the class data, answer the following and use full and complete sentences. 1. Explain why women are carriers for the disease hemophilia. Why do their sons, but not their daughters get the disease? ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2. Describe the difference between how normal traits are inherited and how sex linked traits are inherited. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 3. The information on the data table collected by the class shows how many ACTUAL offspring would have each of the traits. The Punnett squares you completed on page 2, show the PREDICTED ratios. Compare the predicted ratios to the actual results for all three traits. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 4. Notice on the data table that no female has the disease hemophilia. Explain why. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 5. If you knew you were a carrier for hemophilia (or your wife was), would you choose to have children. Explain your reasons. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________