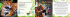Presentation
Transcription
Presentation
Chengdu Forum on UNGGIM Global Map for Sustainable Development: Development and Applications in Urban Hazard Mapping Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China 15 – 17 October 2013 Geospatial Information for the Evaluation of Damage related to Natural Disasters in Mexico ROLANDO OCAMPO ALCÁNTAR Vice-President of the Government Board of INEGI Given its geographic location, Mexico is subject to a huge variety of hydro-meteorological, seismic and volcanic phenomena As being part of the Ring of Fire, the country is affected by intense seismic and volcanic activity SAN ANDREAS FAULT SYSTEM Two-third parts of the country are in a constantly and significantly at seismic risk, due to the subduction of tectonic plates Cocos and North America (Middle America Trench) Sismicidad ASÍSMICA BAJA MEDIA ALTA In terms of volcanic activity, in an historical time, fourteen volcanoes have erupted and are considered still active, or they represent hotspots The territory is often affected by hurricanes that are generated in both Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. On average, 25 meteor arrive yearly to the nearby seas. 4 to 5 out of these 25, penetrate the territory and often cause severe damage. Hurricanes and tropical storms (1949‐2008) In front of the occurrence of Natural Disasters (earthquakes, fire, explosions, material flow, flooding and volcanic eruption), Mexico´s National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI) offers to Federal Government, Entities and Society the integration of statistical and geographical information in order to assist the evaluation of damage and in mitigating the effects caused on population and infrastructure. Juan de Grijalva, Chiapas. 2007 Coordination between INEGI and other institutions, in the event of a disaster. Satellite Imagery Interpretation Measurement •Image interpretation •Report •Statistics It provides information to: Presidency State Governments Federal Government Civil Protection • The information that is available and can be applied to a risk analysis is: • • • • • • Basic geographic information Digital orthophotography Digital Elevation Models Satellite Imagery Natural Resources Datasets Modeling EXAMPLES Juan de Grijalva, Chiapas. 2007 Juan de Grijalva, Chiapas. 2007 Presa Peñitas Juan de Grijalva Hydrographic Network Teziutlán, Puebla. 1999 N° 11 Tropical Depresion, accumulated 900 mm of water. More than 200 people were killed and about 260,000 people were affected in Sierra Norte de Puebla. INEGI. 1999 Special aerophotographic flight Villahermosa, Tabasco.1999 INEGI. 1999. Special aerophotographic flight. In October 1999, the interaction of a Cold Front with Tropical Depression N° 2 caused heavy rains. The situation got worse when three heavy rains made the government take the decision of opening Peñitas´ spillway. Villahermosa was flooded by 40%. 20 000 inhabitants of the state were evacuated and 702 shelters were enabled for 56,411 people. There were a total of 62,300 homes affected and 1,007 schools damaged. Chalco, Estado de México. 2000 INEGI. 2000. Special aerophotographic flight. The levee break of Canal de la Compañía, caused a flood that hit over 12 thousand people. The flooded area was of 444,504 m2. San José del Cabo, Baja California Sur. 2003 Marty Hurricane Category 1, on the Saffir‐Simpson scale, with winds of 130‐150 mph, affected regions of Baja California Sur. INEGI. 2003. Special aerophotographic flight PEMEX DUCT LEAK, FIRE AND EXPLOSION IN SAN MARTIN TEXMELUCAN, PUE., 19/Dec/2010 Secondary damage area Primary damage area Population: 72,515 FIRST EXPLOSION AND START OF THE FIRE 32 houses burned 28 people dead 52 people injured 5,000 people evacuated El Universal ATOYAC RIVER SPILL PATH TAKEN BY THE OIL SPILL ON ATOYAC´S RIVER - 68 KM TO THE DAM MANUEL ÁVILA CAMACHO (VALSEQUILLO) Heróica Puebla de Zaragoza Popocatépetl Volcano 2013 Digital Elevation Model Spatial resolution 3 meters Manuel Hurricane La Pintada, Guerrero. 2013 MODIS Image (September 13, 2013) During September, Mexico was affected by the simultaneous presence of two weather phenomena, Tropical Storm Ingrid in the Gulf of Mexico and Tropical Storm Manuel in the Pacific Ocean (which then also become hurricane). Here are seen both systems in one MODIS image from September 14 of this year, the dense clouds is enhanced in light blue. The interaction between Ingrid and Manuel brought rains in much higher amounts than normal even for these phenomena in much of the country, especially in the state of Guerrero, although several other states also had serious effects. Radar Images September 2013 Acapulco, Guerrero Ciudad Valles, San Luis Potosí The total area afectated was 7.6 has., of which 6.9 has. are located within the area of human settlement of la Pintada, equivalent to 12.8% of the 53.7 hectares of the total area of the town (information resulting from the work of PROCEDE, dated April 2003 survey). TOTAL AREA AFFECTED 7.6 hectares. HUMAN SETTLEMENT AREA OF LA PINTADA 53.7 Has. AFFECTED AREA INSIDE HUMAN SETTLEMENT AREA OF LA PINTADA 6.9 Has. EQUAL TO 12.8% La Pintada, Guerrero. 2013 Before Landslide area : Length 600 m Width 240 m After 多谢