Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption
Transcription
Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption
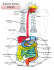
Absorption Movement of monomers, vitamins, minerals & H2O into lumen of digestive tube What happens to food? • Three processes – Digestion – Absorption: the process of moving small molecules across cell membrane and into cells – Elimination • Where does absorption occur? – GI tract Overview of Digestion Digest these Absorb these Absorption occurs along entire GI tract • Stomach: little water, mostly drugs & some vitamins • Small Intestine: Absorption of everything occurs here. • Large intestine: mostly water, some minerals and small fats Specializations encourage absorption • Increased SA (primarily in jejunum) – Plicae circulares: Major folds of intestinal wall. – Villi: Minor folds in close contact with nutrients – The brush border is composed of microvilli Regional Specialization • Duodenum – Few plicae circulares – Short villi • Jejunum – Many plicae circulares – Tall villi – Many lacteals Villi & microvilli How is absorption achieved? Outside cell Carrier loads nutrient on outside of cell . . . Cell membrane Inside cell SIMPLE DIFFUSION Small nutrients (water & small lipids) are absorbed by simple diffusion. Cross into intestinal cells freely. FACILITATED DIFFUSION . . . and then releases it on inside of cell. Some nutrients (water-soluble vitamins) are absorbed by facilitated diffusion. They need a specific carrier to transport them from one side of the cell membrane to the other. Carrier loads nutrient on outside of cell . . . . . . and then releases it on inside of cell. ACTIVE TRANSPORT Some nutrients (glucose & amino acids) must be absorbed actively. These nutrients move against a concentration gradient, which requires energy. Fig. 3-9, p. 81 Carbohydrate absorption • Cotransport into cells (indirect active transport) • Facilitated diffusion into capillaries Carbohydrate Absorption • Monosaccharides enter capillaries within intestinal villi. In the liver, galactose & fructose are converted to glucose. SI Monosaccharides travel to the liver via the bloodstream. Small intestine Stomach Fat Absorption Monoglyceride Short-chain fatty acids Medium-chain fatty acids Glycerol Chylomicrons Micelle Protein Triglyceride Lacteal (lymph) Capillary network Chylomicron Blood vessels To blood To liver Longchain fatty acids Protein absorption • AA & short peptides absorbed via cotransport • Active transport into capillaries • Off to the liver Vitamins & minerals • Absorbed in small and large intestine – Dissolved in lipids – Via carrier proteins – Via diffusion through membrane channels Large intestine: colon + rectum • Undigested food passes illeocecal valve (sphincter) to large intestine • Mostly “indigestible” polysaccharadies, bacteria and H20 remain – Bacteria continue to digest fiber (byproducts =short chain fatty acids + vitamins K & B12) • Absorption of H2O & some nutrients • Elimination Colon histology • Many goblet cells • Few absorptive cells Destination of nutrients • Some lipids and lipid soluble vitamins enter lymph system; This empties into bloodstream • All others enter bloodstream directly • ALL nutrients (save fats) travel to liver first (via portal vein), which stores, processes & regulates their release • Liver filters ALL your blood Head and upper body Nutrient delivery Lungs Pulmonary vein Pulmonary artery Aorta Left side Right side Heart Hepatic artery Hepatic vein Portal vein Liver Digestive tract Lymph Entire body = Arteries = Capillaries = Veins = Lymph vessels